Microsoft - AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator
Sample Questions
Question: 823
Measured Skill: Manage Azure identities and governance (20–25%)
You have the Azure resources shown in the following table.
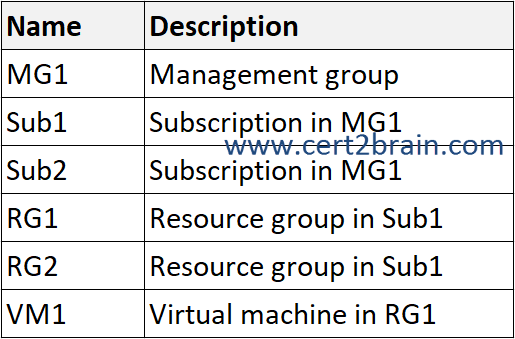
You need to create a custom Azure Policy definition that will use Azure Disk Encryption to automatically encrypt all the virtual machines deployed to Sub1 only.
How should you configure the policy?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each co rrect selection is worth one point.)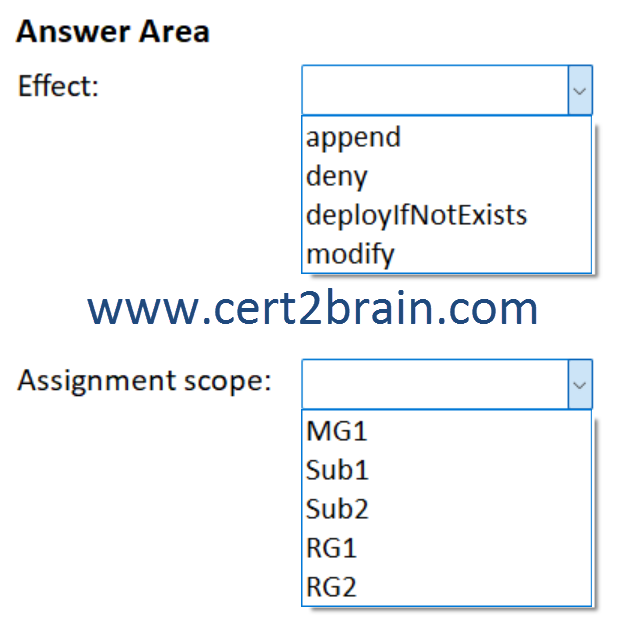
| A | Effect: append
Assignment scope: RG2 |
| B | Effect: deny
Assignment scope: MG1 |
| C | Effect: deployIfNotExists
Assignment scope: Sub1 |
| D | Effect: deployIfNotExists
Assignment scope: MG1 |
| E | Effect: modify
Assignment scope: RG1 |
| F | Effect: modify
Assignment scope: Sub2 |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
Each policy definition in Azure Policy has a single effect in its policyRule. That effect determines what happens when the policy rule is evaluated to match. The effects behave differently if they are for a new resource, an updated resource, or an existing resource.
Similar to auditIfNotExists, a deployIfNotExists policy definition executes a template deployment when the condition is met. Policy assignments with effect set as DeployIfNotExists require a managed identity to do remediation.
deployIfNotExists runs after a configurable delay when a Resource Provider handles a create or update subscription or resource request and returned a success status code. A template deployment occurs if there are no related resources or if the resources defined by existenceCondition don't evaluate to true.
To ensure that the policy applies to all virtual machines in Sub1, we have to assign the policy to Sub1.
References:
What is Azure Policy?
Azure Policy definitions effect basics
Azure Policy definitions deployIfNotExists effect
Question: 824
Measured Skill: Implement and manage virtual networking (15–20%)
You have an Azure subscription named Sub1 that contains the resources shown in the following table.

The subscription contains the users shown in the following table.

VNet2 was created by using the following cmdlet.
New-AzResourceGroupDeploymentStack -Name Deploy1 -ResourceGroupName RG2 -TemplateFile Deploy.bicep -DenySettingsMode DenyDelete -ActionOnUnmanage DetachAll
For VNet2, Access control (IAM) settings are configured as shown in the following exhibit.
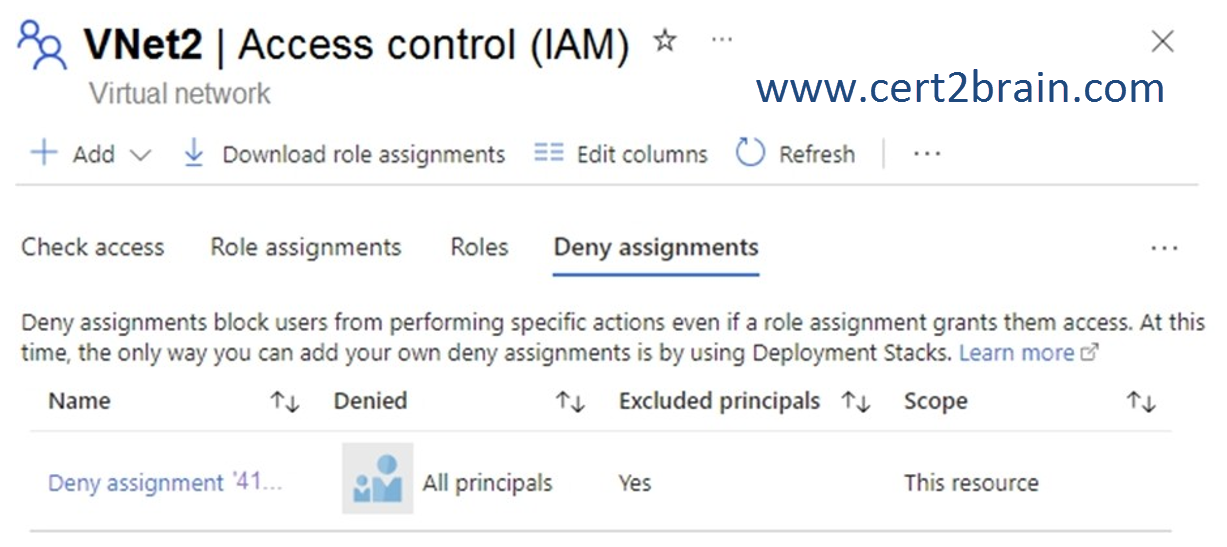
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
(NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)
| A | Admin1 can modify the IP address space of VNet2: Yes
Admin2 can delete Subnet2: Yes
Admin3 can delete VNet2: Yes |
| B | Admin1 can modify the IP address space of VNet2: Yes
Admin2 can delete Subnet2: Yes
Admin3 can delete VNet2: No |
| C | Admin1 can modify the IP address space of VNet2: Yes
Admin2 can delete Subnet2: No
Admin3 can delete VNet2: No |
| D | Admin1 can modify the IP address space of VNet2: No
Admin2 can delete Subnet2: Yes
Admin3 can delete VNet2: No |
| E | Admin1 can modify the IP address space of VNet2: No
Admin2 can delete Subnet2: No
Admin3 can delete VNet2: Yes |
| F | Admin1 can modify the IP address space of VNet2: No
Admin2 can delete Subnet2: No
Admin3 can delete VNet2: No |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
Admin1 has the Network Contributor role assigned for Sub1. The Network Contributor allows Admin1 to manage virtual networks in Sub1, but does not grant access to them.
The deny assignment added by the deployment stack Deployment1 prevents all users including owners from deleting VNet2 (-DenySettingsMode DenyDelete) but does not prevent modifications. If DenySettingsMode were set to DenyWriteAndDelete Admin1 could not modify the IP address space of VNet2.
Reference: List Azure deny assignments
Question: 825
Measured Skill: Manage Azure identities and governance (20–25%)
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant named contoso.com that has the External collaboration settings shown in the following exhibit.
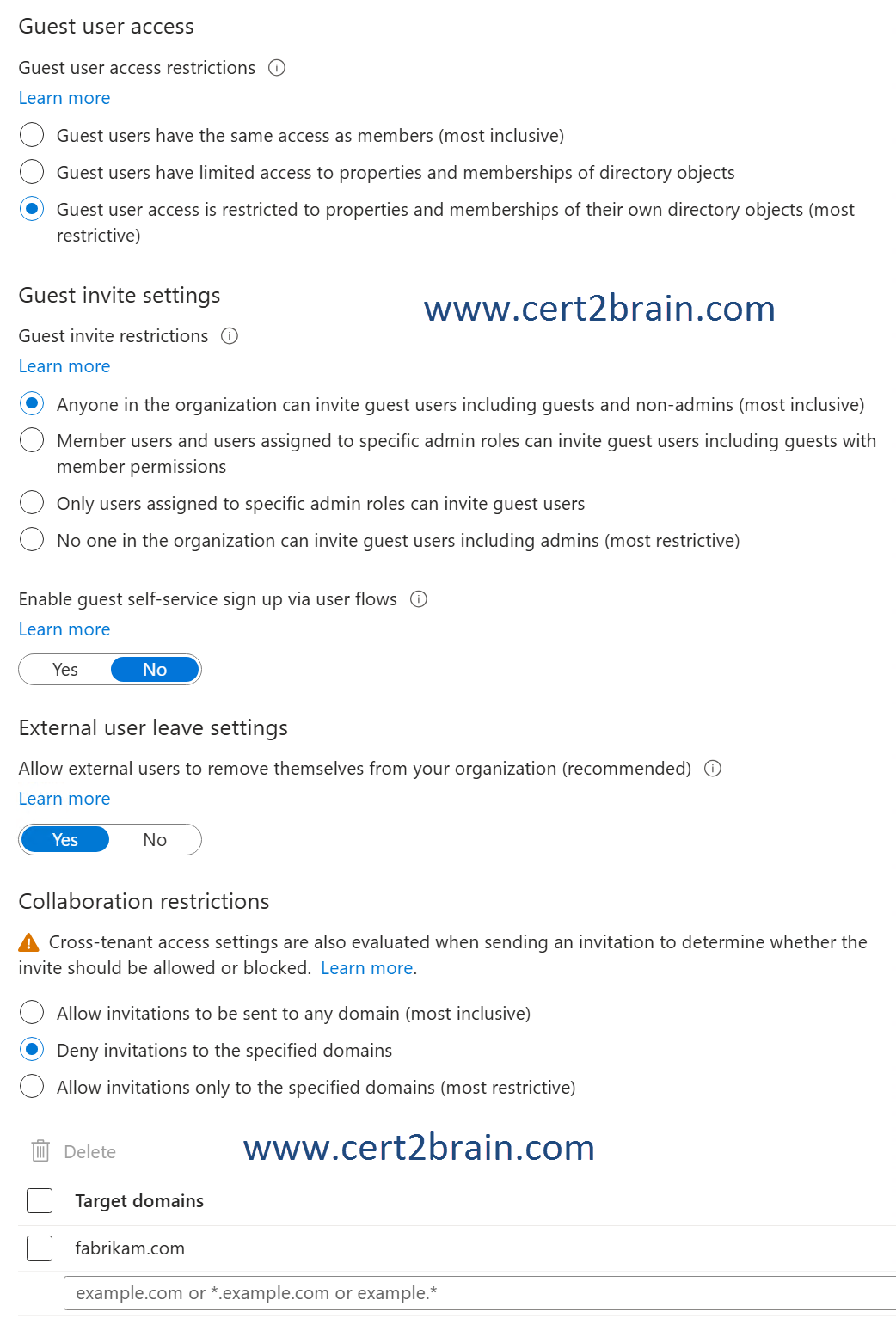
The tenant contains the users shown in the following table.

User2 is an invited guest of User1.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
(NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)
| A | User2 can view the Manager property of User1: Yes
User2 can invite a user named user3@northwindtraders.com to collaborate: Yes
User2 can create a Microsoft 365 group in the contoso.com tenant: Yes |
| B | User2 can view the Manager property of User1: Yes
User2 can invite a user named user3@northwindtraders.com to collaborate: Yes
User2 can create a Microsoft 365 group in the contoso.com tenant: No |
| C | User2 can view the Manager property of User1: Yes
User2 can invite a user named user3@northwindtraders.com to collaborate: No
User2 can create a Microsoft 365 group in the contoso.com tenant: Yes |
| D | User2 can view the Manager property of User1: No
User2 can invite a user named user3@northwindtraders.com to collaborate: Yes
User2 can create a Microsoft 365 group in the contoso.com tenant: No |
| E | User2 can view the Manager property of User1: No
User2 can invite a user named user3@northwindtraders.com to collaborate: Yes
User2 can create a Microsoft 365 group in the contoso.com tenant: Yes |
| F | User2 can view the Manager property of User1: No
User2 can invite a user named user3@northwindtraders.com to collaborate: No
User2 can create a Microsoft 365 group in the contoso.com tenant: No |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
User2 is a guest user from the fabrikam.com tenant. User2 has no role assigned in the contoso.com tenant.
Guest user access is restricted to properties and memberships of their own directory objects. User2 cannot view any properties of User1.
Anyone in the organization can invite guest users including guests and non-admins. User2 can invite a user named user3@northwindtraders.com to collaborate.
User2 cannot create a Microsoft 365 group in the contoso.com tenant. User2 must have at least the Groups Administrator or User Administrator role assigned to create groups.
References:
Configure external collaboration settings for B2B in Microsoft Entra External ID
Manage Microsoft Entra groups and group membership
Groups least privileged roles
Question: 826
Measured Skill: Manage Azure identities and governance (20–25%)
You need to implement multiple Azure subscriptions for production and development environments. The solution must meet the following requirements:
- Control costs by limiting the number of high-cost resources that can be provisioned in the subscriptions.
- Group all the resources by application for cost reporting.
- Control costs by monitoring resource usage.
What should you configure for each requirement?
(To answer, drag the appropriate options to the correct requirements. Each option may be used once, more than once, or not at all. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)
| A | Control costs by limiting high-cost resources: A management group
Group all the resources by application for cost reporting: A resource group
Control costs by monitoring resource usage: A budget |
| B | Control costs by limiting high-cost resources: A resource group
Group all the resources by application for cost reporting: A tag
Control costs by monitoring resource usage: A policy |
| C | Control costs by limiting high-cost resources: A budget
Group all the resources by application for cost reporting: A management group
Control costs by monitoring resource usage: A tag |
| D | Control costs by limiting high-cost resources: A policy
Group all the resources by application for cost reporting: A resource group
Control costs by monitoring resource usage: A management group |
| E | Control costs by limiting high-cost resources: A policy
Group all the resources by application for cost reporting: A tag
Control costs by monitoring resource usage: A budget |
| F | Control costs by limiting high-cost resources: A tag
Group all the resources by application for cost reporting: A policy
Control costs by monitoring resource usage: A resource group |
Correct answer: EExplanation:
To limit the number of high-cost resources that can be provisioned, we should make use of Azure Policy. Azure Policy evaluates resources and actions in Azure by comparing the properties of those resources to business rules. These business rules, described in JSON format, are known as policy definitions. Common use cases for Azure Policy include implementing governance for resource consistency, regulatory compliance, security, cost, and management. Policy definitions for these common use cases are already available in your Azure environment as built-ins to help you get started.
The following are examples for policy definitions that can help to control costs by limiting high-cost resources:
- Not Allowed Resource Types
- Allowed virtual machine size SKUs
- Allowed App Services Plan SKUs
To group resources by application for cost reporting, we should add tags to the resources. Tags are metadata elements that you apply to your Azure resources. They are key-value pairs that help you identify resources based on settings that are relevant to your organization. If you want to track the deployment environment for your resources, add a key named Environment. To identify the resources deployed to production, give them a value of Production. The full key-value pair is Environment = Production.
To control costs by monitoring resource usage, we should implement a budget. Budgets are commonly used as part of cost control. Budgets can be scoped in Azure. For instance, you could narrow your budget view based on subscription, resource groups, or a collection of resources. Besides using the budgets API to send email notifications when a budget threshold is reached, you can also use Azure Monitor action groups. Action groups trigger a coordinated set of actions in response to a budget event.
References:
What is Azure Policy?
Use tags to organize your Azure resources and management hierarchy
Manage costs with budgets
Question: 827
Measured Skill: Deploy and manage Azure compute resources (20–25%)
You have a new Azure subscription.
You plan to deploy the resources shown in the following table.
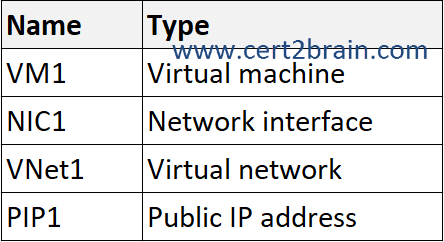
You need to create an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template to automate the deployment. The solution must ensure that all the resources are deployed successfully.
In which order should the ARM template deploy the resources?
(To answer, move all resources from the list of resources to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order. NOTE: More than one order of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct orders you select.)
| A | Sequence: PIP1, NIC1, VNet1, VM1 |
| B | Sequence: NIC1, PIP1, VNet1, VM1 |
| C | Sequence: VNet1, PIP1, NIC1, VM1 |
| D | Sequence: VM1, VNet1, NIC1, PIP1 |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
When deploying resources, you may need to make sure some resources exist before other resources. For example, you need a logical SQL server before deploying a database. You establish this relationship by marking one resource as dependent on the other resource. Use the dependsOn element to define an explicit dependency.
First and second, we need to create the virtual network (VNet1) and the public IP address (PIP1). It doesn't matter which of the two resources we create first as they don't directly depend on each other. But, both must exist before a the network interface (NIC1) can use them.
Third, we create the network interface (NIC1). The network interface requires a subnet within a virtual network and an IP address to be configured before it can be created.
Lastly, we create the virtual machine (VM1). The VM requires the network interface to connect to the virtual network.
Reference: Define the order for deploying resources in ARM templates