Microsoft - AZ-800: Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
Sample Questions
Question: 321
Measured Skill: Deploy and manage Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) in on-premises and cloud environments (30-35%)
Your network contains an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest named contoso.com. The forest contains the users shown in the following table.
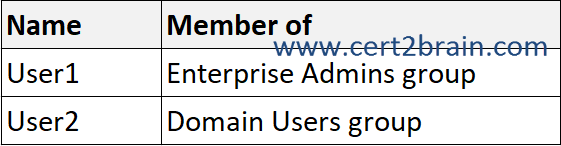
You have a workgroup server named Server1 that runs Windows Server and contains the local users shown in the following table.
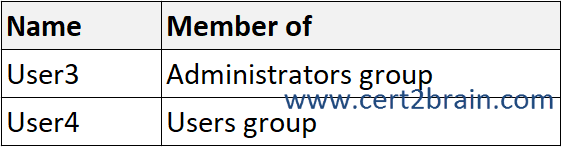
You promote Server1 to the first domain controller in a new child domain named east.contoso.com.
Which users can sign in to Server1 locally?| A | User1 only |
| B | User3 only |
| C | User1 and User2 only |
| D | User1 and User3 only |
| E | User3 and User4 only |
| F | User1, User2, User3 and User4 |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
Once a server is promoted to a domain controller, it does not have local user or administrator accounts anymore. The local Security Account Manager (SAM) database is removed. Only domain accounts and the special Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) account can sign. "Sign in locally" must be understood as sign in to the local device.
The "Allow log on locally" user rights assignments policy of the Default Domain Controllers Policy contains the following groups:
- Account Operators
- Administrators
- Backup Operators
- Print Operators
- Server Operators
The Administrators group default members are: Administrator, Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins
References:
Active Directory security groups
Allow log on locally
Question: 322
Measured Skill: Deploy and manage Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) in on-premises and cloud environments (30-35%)
Your network contains two Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forests named contoso.com and adatum.com. A two-way external trust exists between contoso.com and adatum.com.
The forests contain the servers shown in the following table.
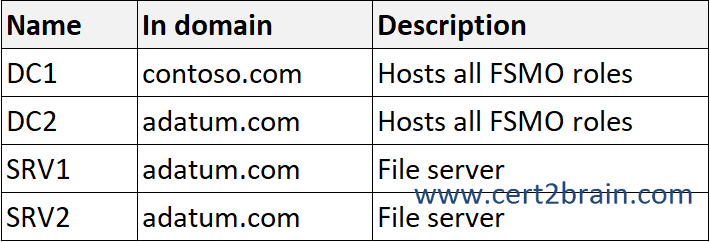
You need to ensure that users from contoso.com can access only shared resources hosted on SRV1. The solution must meet the following requirements:
- Ensure that users from adatum.com can access the resources hosted in contoso.com.
- Prevent the contoso.com users from accessing any other resources in adatum.com.
What should you do?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)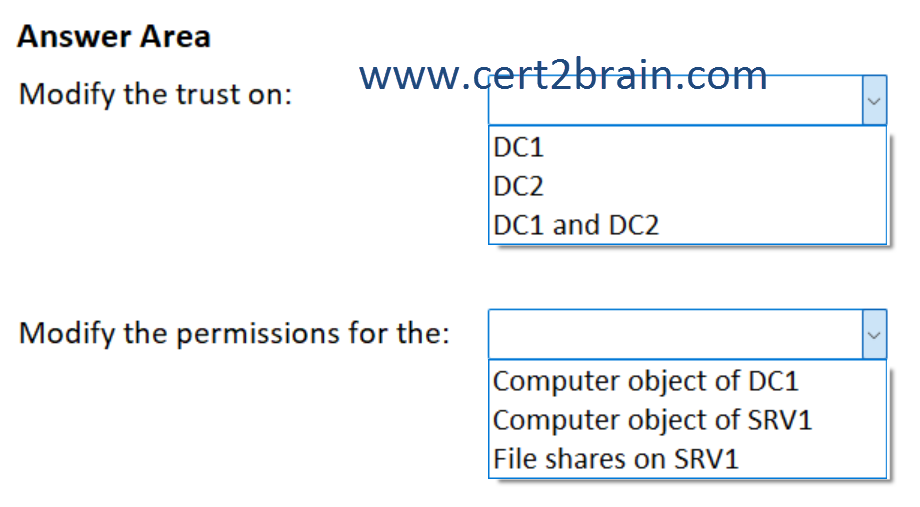
| A | Modify the trust on: DC1
Modify the permissions for the: File shares on SRV1 |
| B | Modify the trust on: DC1
Modify the permissions for the: Computer object of DC1 |
| C | Modify the trust on: DC2
Modify the permissions for the: Computer object of SRV1 |
| D | Modify the trust on: DC2
Modify the permissions for the: Computer object of DC1 |
| E | Modify the trust on: DC1 and DC2
Modify the permissions for the: Computer object of SRV1 |
| F | Modify the trust on: DC1 and DC2
Modify the permissions for the: File shares on SRV1 |
Correct answer: EExplanation:
We need to replace the two-way external trust between contoso.com and adatum.com by a forest trust and enable selective authorization. Then we need to configure the security settings from the computer account object of the file server (srv1.adatum.com) to allow the CONTOSO\Domain Users group to authenticate.
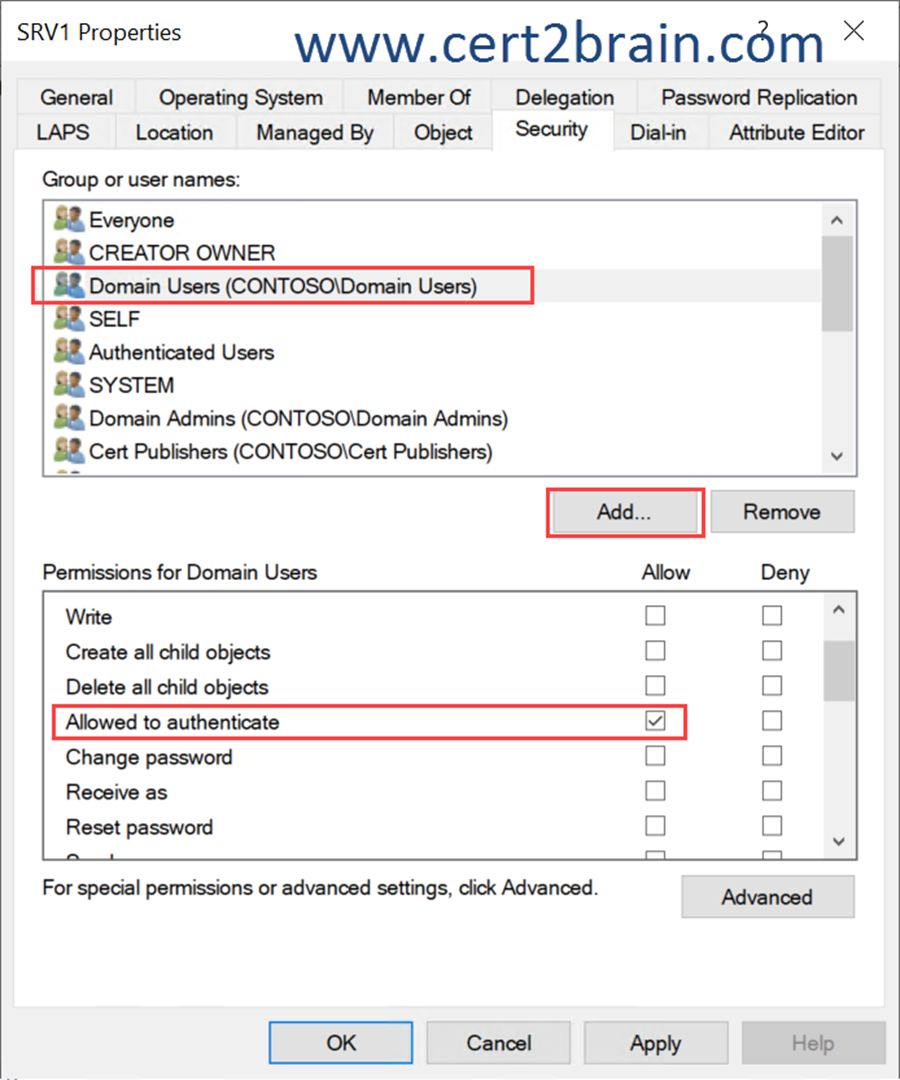
This ensures that users of the contoso.com domain within adatum.com can only be authenticated on srv1.
Reference: How trust relationships work for forests in Active Directory
Question: 323
Measured Skill: Manage virtual machines and containers (15-20%)
You have 100 on-premises servers that run Windows Server and are Azure Arc-enabled.
You have an Azure subscription.
You deploy a Custom Script Extension to the servers by using the following Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template.
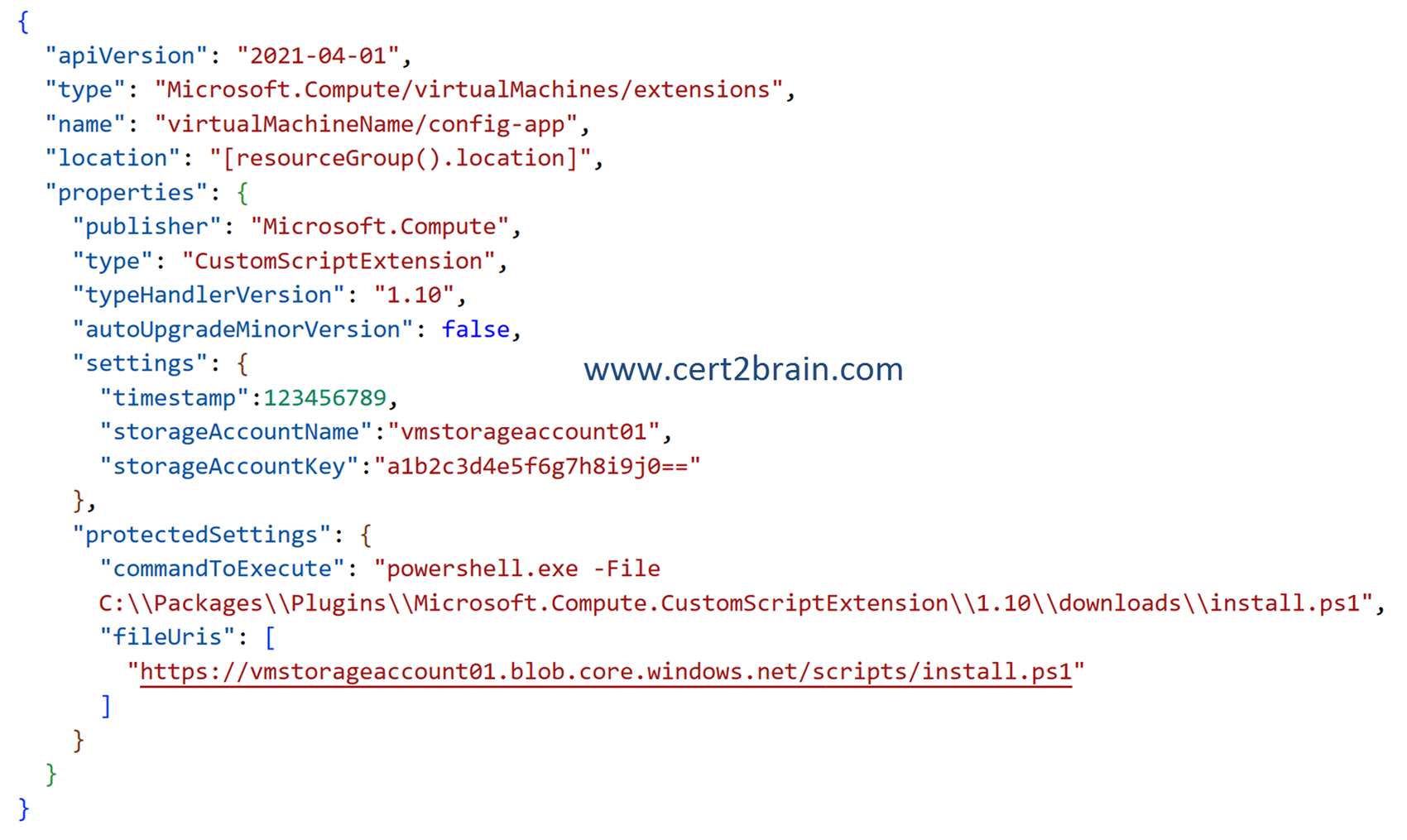
You regenerate the storage account key and update the template.
You need to meet the following requirements:
- Ensure that the script runs again on the servers.
- Minimize the risk of the key being compromised on the servers.
What should you do?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)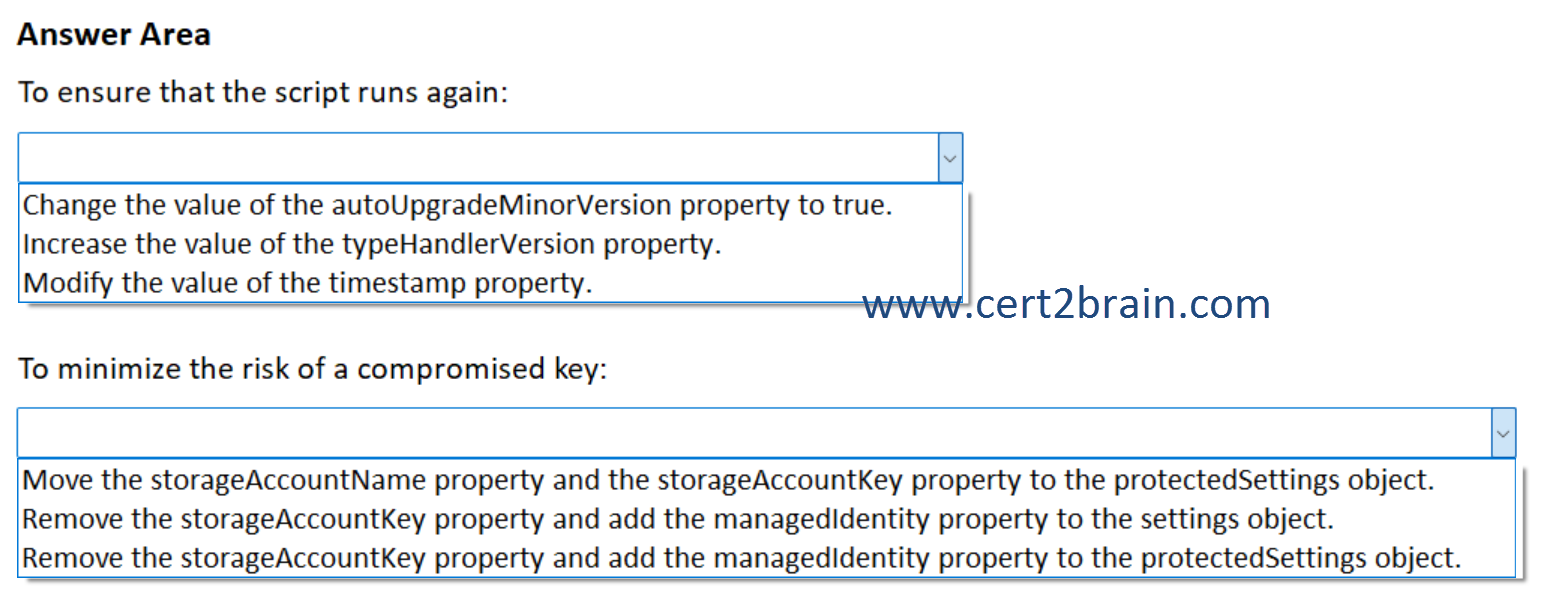
| A | To ensure that the script runs again: Change the value of the autoUpgradeMinorVersion property to true.
To minimize the risk of a compromised key: Remove the storageAccountKey property and add the managedIdentity property to the settings object. |
| B | To ensure that the script runs again: Change the value of the autoUpgradeMinorVersion property to true.
To minimize the risk of a compromised key: Remove the storageAccountKey property and add the managedIdentity property to the protectedSettings object. |
| C | To ensure that the script runs again: Increase the value of the typeHandlerVersion property.
To minimize the risk of a compromised key: Remove the storageAccountKey property and add the managedIdentity property to the settings object. |
| D | To ensure that the script runs again: Increase the value of the typeHandlerVersion property.
To minimize the risk of a compromised key: Move the storageAccountName property and the storageAccountKey property to the protectedSettings object. |
| E | To ensure that the script runs again: Modify the value of the timestamp property.
To minimize the risk of a compromised key: Remove the storageAccountKey property and add the managedIdentity property to the protectedSettings object. |
| F | To ensure that the script runs again: Modify the value of the timestamp property.
To minimize the risk of a compromised key: Move the storageAccountName property and the storageAccountKey property to the protectedSettings object. |
Correct answer: FExplanation:
Only one version of an extension can be installed on a VM at a time. Specifying a custom script twice in the same Azure Resource Manager template for the same VM fails.
To trigger a rerun of the script you need to change the value of the timestamp property. Any integer value is acceptable, as long as it's different from the previous value.
You can store sensitive data in a protected configuration, which is encrypted and only decrypted inside the VM. The protected configuration is useful when the execution command includes secrets such as a password or a shared access signature (SAS) file reference. Here's an example:

If you plan to use the storageAccountName and storageAccountKey properties, these properties must be collocated in protectedSettings.
References:
Custom Script Extension for Windows
VirtualMachineScaleSetExtension interface
Question: 324
Measured Skill: Manage virtual machines and containers (15-20%)
You deploy a Windows Server container host.
You need to create a container image that will be based on the Nano Server base image and will contain a custom file.
Which four commands should you run in sequence?
(To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.)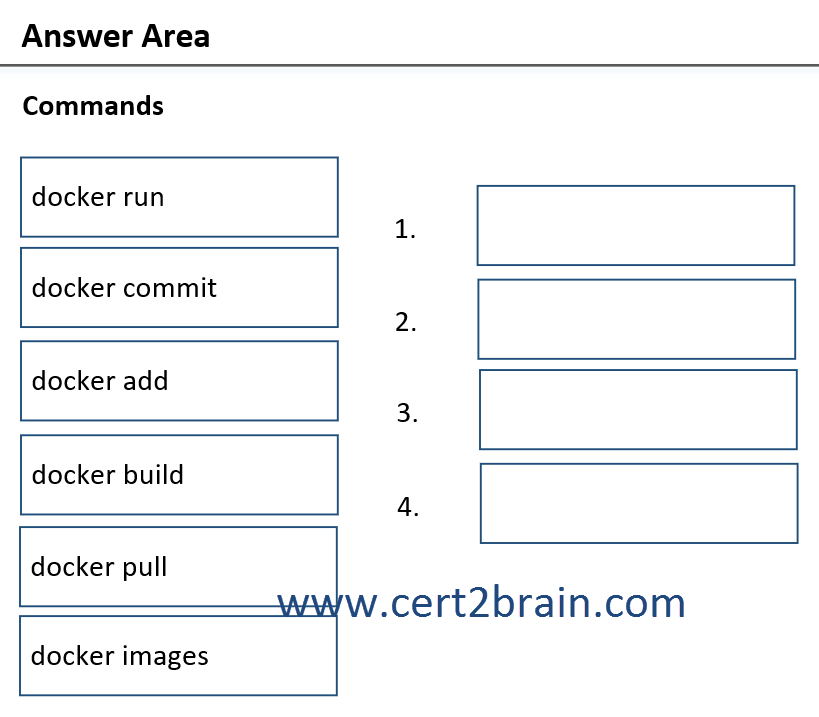
| A | 1: docker images
2: docker add
3: docker build
4: docker run |
| B | 1: docker pull
2: docker add
3: docker commit
4: docker run |
| C | 1: docker build
2: docker pull
3: docker commit
4: docker run |
| D | 1: docker pull
2: docker add
3: docker commit
4: docker build |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
All containers are created from container images. Microsoft offers several starter images, called base images, to choose from.
You can use the following procedure to pull the lightweight Nano Server base image, or in other words, to download and install that image.
Open a console window such as the built-in Command Prompt, PowerShell, or Windows Terminal.
Run the following command to download and install the base image:
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/windows/nanoserver:ltsc2022
The docker add command is used to copy files/directories into a Docker image.
The docker commit command create a new image from a container's changes.
The docker run command creates and starts a container from the newly created image.
Reference: Get started: Run your first Windows container
Question: 325
Measured Skill: Manage Windows Servers and workloads in a hybrid environment (10-15%)
You have an on-premises server named Server1 that runs Windows Server and is managed by using Windows Admin Center.
You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual network named VNet1.
You need to connect Server1 to VNet1 by using an Azure Network Adapter.
What should you do first in Windows Admin Center?| A | Select Roles & features and install the DirectAccess and VPN (RAS) role service. |
| B | Select Register and register Windows Admin Center with Azure. |
| C | Select Extensions and install the Azure Cloud Shell extension. |
| D | Select Internet Access and modify the Internet Access settings. |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
A lot of workloads running on-premises and in multi-cloud environments require connections to virtual machines (VMs) running in Microsoft Azure. To connect a server to an Azure Virtual Network, you have several options, including Site-to-Site VPN, Azure Express Route, and Point-to-Site VPN.
Windows Admin Center and Azure Network Adapter provide a one-click experience to connect the server with your virtual network using a Point-to-Site VPN connection. The process automates configuring the virtual network gateway and the on-premises VPN client.
As a requirement to deploy Azure Network Adapter, we need to integrate Windows Admin Center with Azure.
Reference: Use Azure Network Adapter to connect a server to an Azure Virtual Network