Microsoft - AZ-801: Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
Sample Questions
Question: 305
Measured Skill: Migrate servers and workloads (20-25%)
Your network contains two Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forests named contoso.com and fabrikam.com. Contoso.com includes the groups shown in the following table.
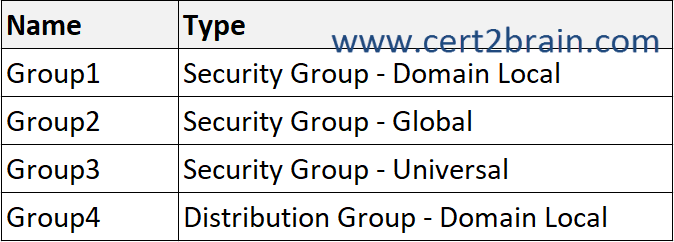
You need to migrate the groups to fabrikam.com by using the Active Directory Migration Tool (ADMT).
Which groups can be migrated and which groups can have the sIDHistory attribute populated after the migration?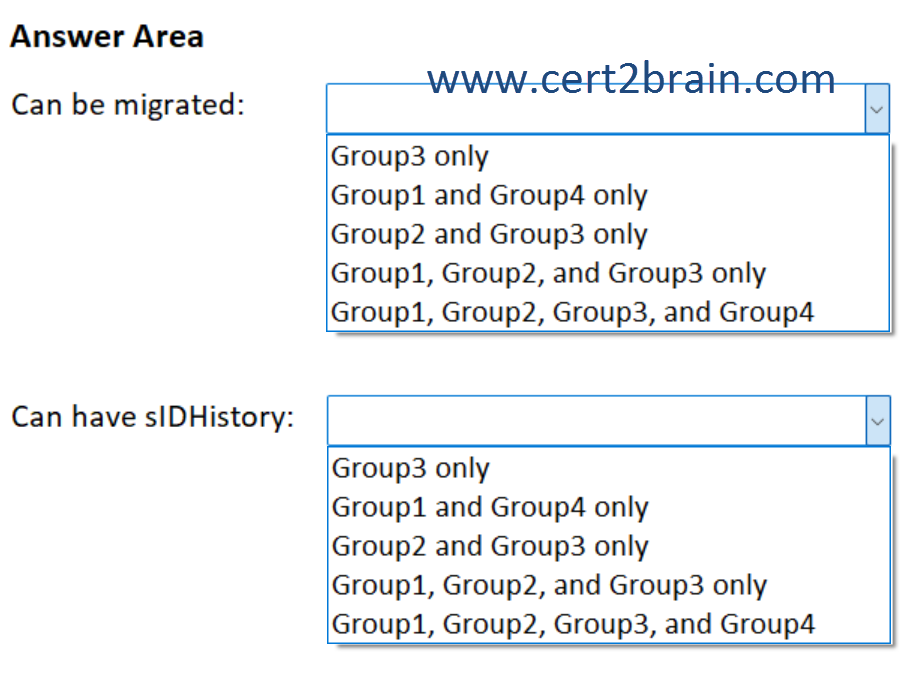
| A | Can be migrated: Group3 only
Can have sIDHistory: Group2 and Group3 only |
| B | Can be migrated: Group1 and Group4 only
Can have sIDHistory: Group3 only |
| C | Can be migrated: Group2 and Group3 only
Can have sIDHistory: Group1 and Group4 only |
| D | Can be migrated: Group1, Group2, and Group3 only
Can have sIDHistory: Group1, Group2, and Group3 only |
| E | Can be migrated: Group1, Group2, Group3, and Group4
Can have sIDHistory: Group2 and Group3 only |
| F | Can be migrated: Group1, Group2, Group3, and Group4
Can have sIDHistory: Group1, Group2, Group3, and Group4 |
Correct answer: EExplanation:
The Active Directory Migration Tool version simplifies the process of migrating objects and restructuring tasks in an Active Directory Domain Service (AD DS) environment. You can use ADMT to migrate users, groups, and computers between AD DS domains in different forests (inter-forest migration) or between AD DS domains in the same forest (intra-forest migration). ADMT can also perform security translation (to migrate local user profiles) when performing inter-forest migrations.
ADMT can migrate security and distribution groups of all scopes:
- Domain Local
- Global
- Universal
ADMT can populate the sIDHistory only for security principals that can be used for authorization across domains, this includes global security groups and universal security groups. Domain local groups are valid only in their source domain and distribution groups aren't security principals.
References:
Active Directory Migration Tool (ADMT) Guide: Migrating and Restructuring Active Directory Domains
Active Directory security groups
Security identifiers
Question: 306
Measured Skill: Monitor and troubleshoot Windows Server environments (20-25%)
You have an Azure subscription.
Your on-premises network connects to Azure by using an Azure VPN gateway named VPN1.
You need to monitor the Azure gateway health probe for VPN1.
Which TCP port should you use?| A | 443 |
| B | 1723 |
| C | 3389 |
| D | 8081 |
| E | 65500 |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
Azure VPN Gateway is a specific type of virtual network gateway that is used to send encrypted traffic between an Azure virtual network and an on-premises location over the public Internet.
Azure VPN Gateway exposes a health probe endpoint that can be monitored to verify gateway availability and health. The Azure gateway health probe listens on TCP port 8081 and is used specifically for monitoring and diagnostics. It is not used for VPN tunnels themselves.
References:
What is Azure VPN Gateway?
Step 7: Verify the Azure gateway health probe
Question: 307
Measured Skill: Monitor and troubleshoot Windows Server environments (20-25%)
You have an Azure subscription. The subscription contains a Log Analytics workspace named Workspace1 and 100 virtual machines that run Windows Server.
You enable Microsoft Defender for Servers Plan 2 and configure Defender for Servers to monitor for Windows file and registry changes on the virtual machines.
You need to query the detected file and registry changes.
Which table should you query?| A | ASimFileEventLogs |
| B | MDCDetectionFimEvents |
| C | ASimRegistryEventLogs |
| D | DeviceRegistryEvents |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
The file integrity monitoring feature in Microsoft Defender for Cloud's Defender for Servers Plan 2, scans operating system files, Windows registries, application software, and Linux system files. It analyzes these files for changes that might indicate an attack.
File integrity monitoring helps you to:
- Meet compliance requirements. Regulatory compliance standards such as PCI-DSS and ISO 17799 often require file integrity monitoring.
- Improve posture and identify potential security issues by detecting suspicious changes to files.
Defender for Cloud sends the detected changes to the selected Log Analytics workspace. Those changes are stored in the MDCDetectionFimEvents table.
References:
File integrity monitoring
Enable File Integrity Monitoring
Question: 308
Measured Skill: Monitor and troubleshoot Windows Server environments (20-25%)
You have an Azure subscription. The subscription contains a virtual machine named Server1 that runs Windows Server.
You create a new Log Analytics workspace named Workspace1.
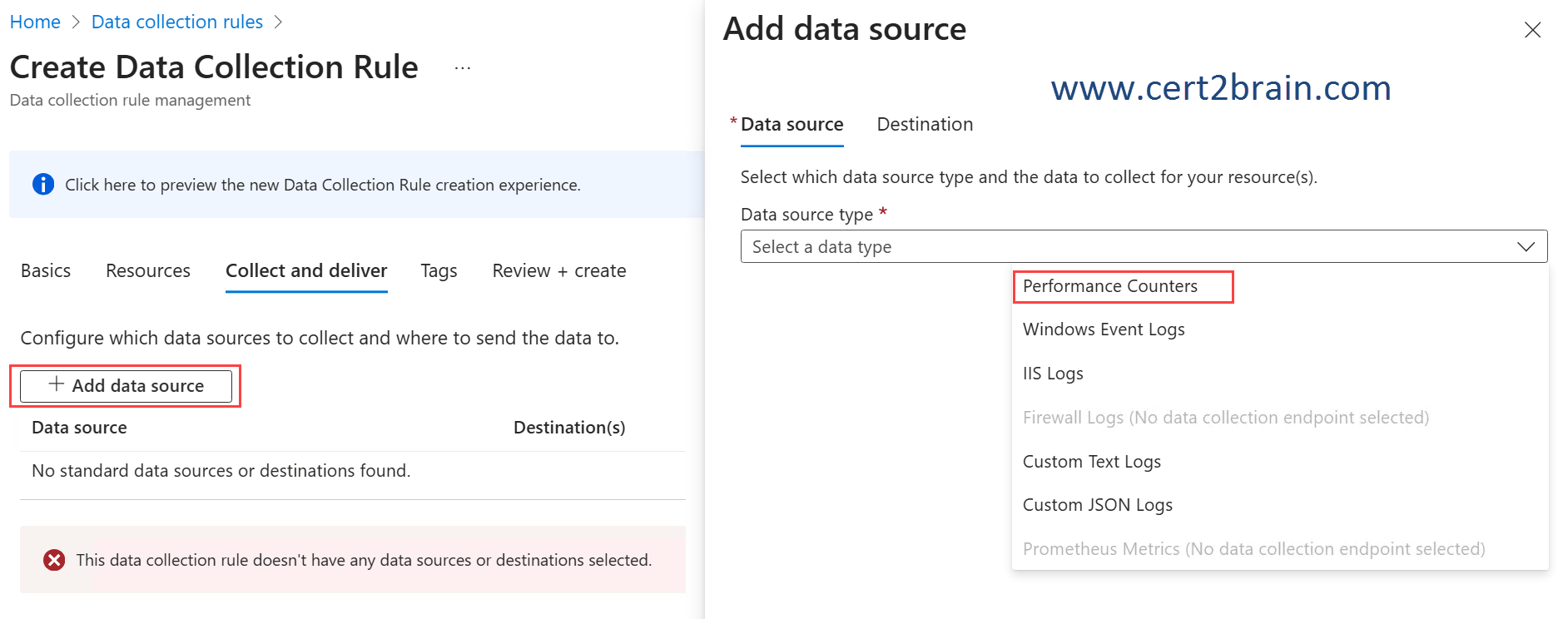
You need to collect performance metrics for Server1 by using Azure Monitor.
What should you do next?| A | Regenerate the secondary key. |
| B | Install the Azure Connected Machine agent. |
| C | Create a data collection rule (DCR). |
| D | Deploy and configure Windows Event Forwarding. |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
In Azure Monitor, performance metrics and logs from virtual machines are collected by using the Azure Monitor Agent (AMA), which is configured and controlled through Data Collection Rules (DCRs).
Data collection rules (DCRs) are part of an Extract, transform, and load (ETL)-like data collection process that improves on legacy data collection methods for Azure Monitor.
Data collection rules (DCRs) are stored in Azure so they can be centrally deployed and managed like any other Azure resource. They provide a consistent and centralized way to define and customize different data collection scenarios.
References:
Data collection rules (DCRs) in Azure Monitor
Create data collection rules (DCRs) in Azure Monitor
Question: 309
Measured Skill: Migrate servers and workloads (20-25%)
You have a Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services deployment that includes the servers shown in the following table.
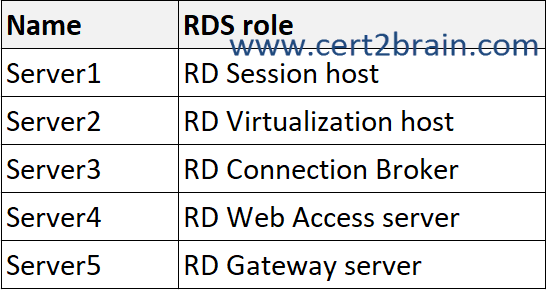
You need to upgrade the Remote Desktop Services deployment to Windows Server 2025.
Which Server must you upgrade first?| A | Server1 |
| B | Server2 |
| C | Server3 |
| D | Server4 |
| E | Server5 |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
You can upgrade to a newer version of Windows Server by two versions at a time. For example, you can upgrade to Windows Server 2025 from Windows Server 2019.
In order to keep the downtime to a minimum, use the following guide:
RD Connection Broker servers should be upgraded first. If you have an active/active configuration, remove all but one server from the deployment and perform an in-place upgrade. Perform upgrades on the remaining RD Connection Broker servers offline and then reapply them to the deployment. The deployment isn't available during the RD Connection Broker servers' upgrade.
RD License servers should be upgraded before you upgrade your RD Session Host servers.
RD Session Host servers can be upgraded next. Avoid downtime during upgrade by splitting the servers to be upgraded into steps as detailed. All will be functional after the upgrade.
RD Virtualization Host servers can be upgraded next.
RD Web Access servers can be upgraded anytime.
RD Gateway servers can be upgraded anytime.
Reference: Upgrade Remote Desktop Services deployments