Archive - MS-101: Microsoft 365 Mobility and Security
Sample Questions
Question: 484
Measured Skill: Implement Microsoft 365 Security and Threat Management (20-25%)
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription.
You need to be alerted when Microsoft 365 Defender detects high-severity incidents.
What should you use?| A | A threat policy |
| B | A custom detection rule |
| C | An alert policy |
| D | A notification rule |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
You can configure Microsoft 365 Defender to send email notifications to specified recipients for new alerts. This feature enables you to identify a group of individuals who will immediately be informed and can act on alerts based on their severity.
You can set the alert severity levels that trigger notifications. You can also add or remove recipients of the email notification. New recipients get notified about alerts triggered after they're added.
Create rules for alert notifications
You can create rules that determine the devices and alert severities to send email notifications for and the notification recipients.
Go to Microsoft 365 Defender and sign in using an account with the Security administrator or Global administrator role assigned.
In the navigation pane, select Settings > Endpoints > General > Email notifications.
Click Add item.
Specify the General information:
Rule name - Specify a name for the notification rule.
Include organization name - Specify the customer name that appears on the email notification.
Include tenant-specific portal link - Adds a link with the tenant ID to allow access to a specific tenant.
Include device information - Includes the device name in the email alert body.
Devices - Choose whether to notify recipients for alerts on all devices (Global administrator role only) or on selected device groups.
Alert severity - Choose the alert severity level.
Click Next.
Enter the recipient's email address then click Add recipient. You can add multiple email addresses.
Check that email recipients can receive the email notifications by selecting Send test email.
Click Save notification rule.
Reference: Configure alert notifications in Microsoft 365 Defender
Question: 485
Measured Skill: Implement Modern Device Services (40-45%)
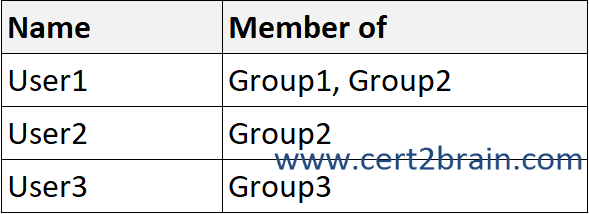
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that contains the users shown in the following table.
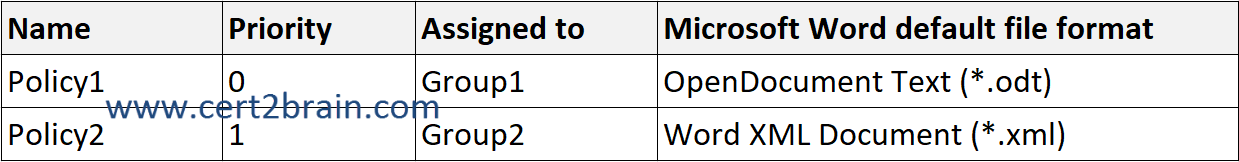
In Microsoft Intune, you have the Policies for Office apps configurations shown in the following table.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
(NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)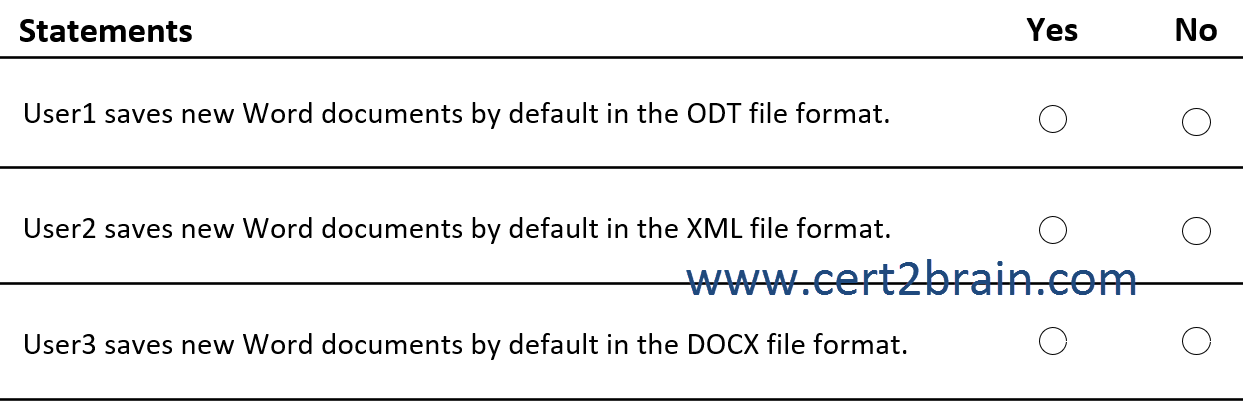
| A | User1 saves new Word documents by default in the ODT file format: Yes
User2 saves new Word documents by default in the XML file format: Yes
User3 saves new Word documents by default in the DOCX file format: Yes |
| B | User1 saves new Word documents by default in the ODT file format: Yes
User2 saves new Word documents by default in the XML file format: Yes
User3 saves new Word documents by default in the DOCX file format: No |
| C | User1 saves new Word documents by default in the ODT file format: Yes
User2 saves new Word documents by default in the XML file format: No
User3 saves new Word documents by default in the DOCX file format: Yes |
| D | User1 saves new Word documents by default in the ODT file format: No
User2 saves new Word documents by default in the XML file format: Yes
User3 saves new Word documents by default in the DOCX file format: No |
| E | User1 saves new Word documents by default in the ODT file format: No
User2 saves new Word documents by default in the XML file format: Yes
User3 saves new Word documents by default in the DOCX file format: Yes |
| F | User1 saves new Word documents by default in the ODT file format: No
User2 saves new Word documents by default in the XML file format: No
User3 saves new Word documents by default in the DOCX file format: No |
Correct answer: AExplanation:
User1 is a member of Group1 and Group2. Both groups have a policy assigned. The highest priority policy will take precedence. User1 will save Word documents in the ODT file format.
User2 is a member of Group2, which has Policy2 assigned. Policy2 sets the default file format to XML.
User3 does not have a policy assigned and will save Word documents in the default file fomrat which is DOCX.
Reference: Policies for Office apps
Question: 486
Measured Skill: Implement Microsoft 365 Security and Threat Management (20-25%)
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription.
You need to ensure that administrators receive an email when Microsoft 365 Defender detects a sign-in from a risky IP address.
What should you create?| A | An incident assignment filter |
| B | A vulnerability notification rule |
| C | An incident notification rule |
| D | An anomaly detection policy |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
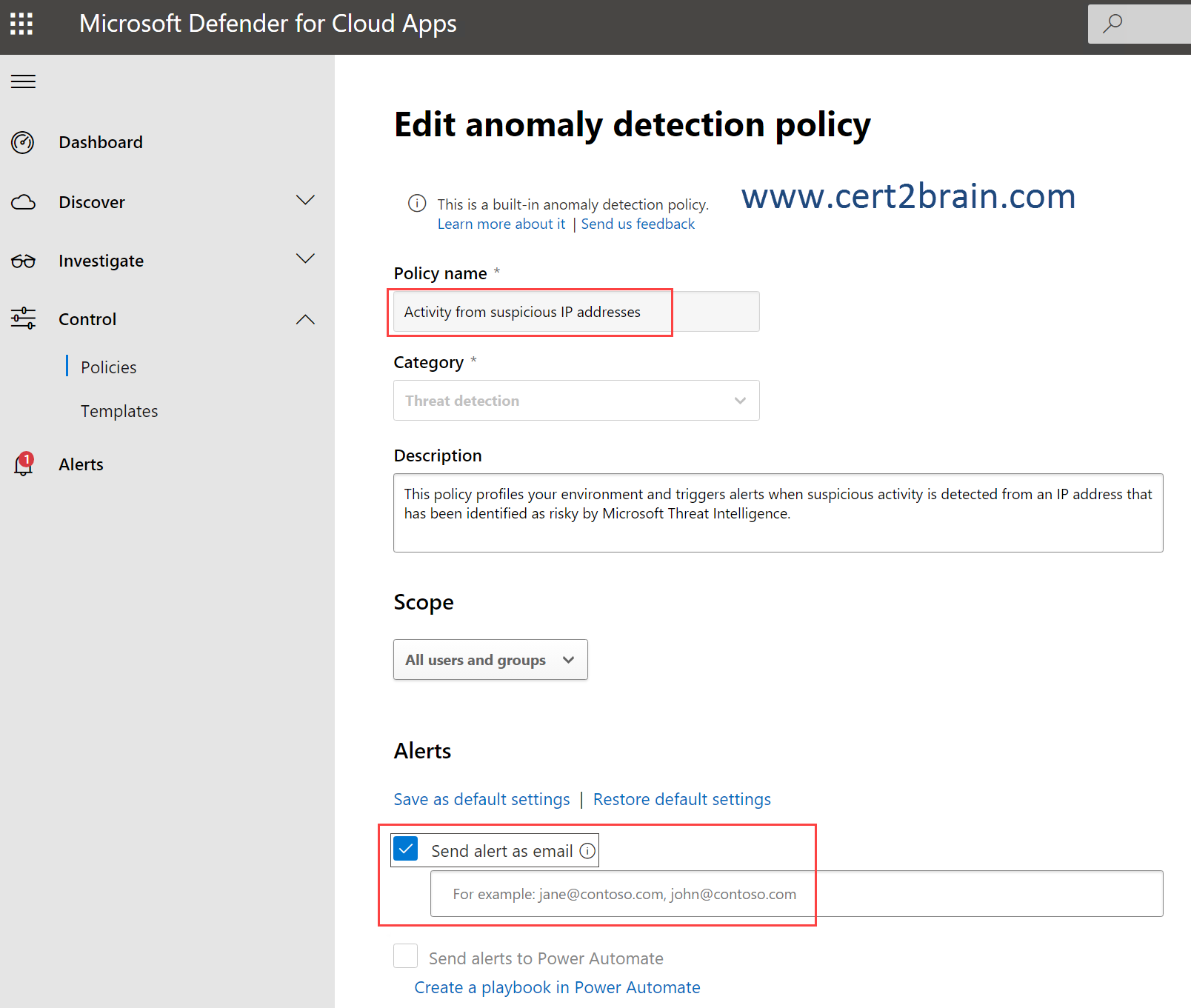
We should configure email alerts for the built-in anomaly detection policy "Activity from suspicious IP addresses" as shown below.
Question: 487
Measured Skill: Implement Microsoft 365 Security and Threat Management (20-25%)
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that uses Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
You need to ensure that users are prevented from opening or downloading malicious files from Microsoft Teams, OneDrive, or SharePoint Online.
What should you do?| A | Configure the Safe Links global settings. |
| B | Create a new Anti-malware policy. |
| C | Configure the Safe Attachments global settings. |
| D | Create a new Anti-phishing policy. |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
In organizations with Microsoft Defender for Office 365, Safe Attachments for Office 365 for SharePoint, OneDrive, and Microsoft Teams protects your organization from inadvertently sharing malicious files.
We need to enable Defender for Office 365 for SharePoint, OneDrive and Microsoft Teams in the Global Settings of the Safe Attachments feature as shown below.
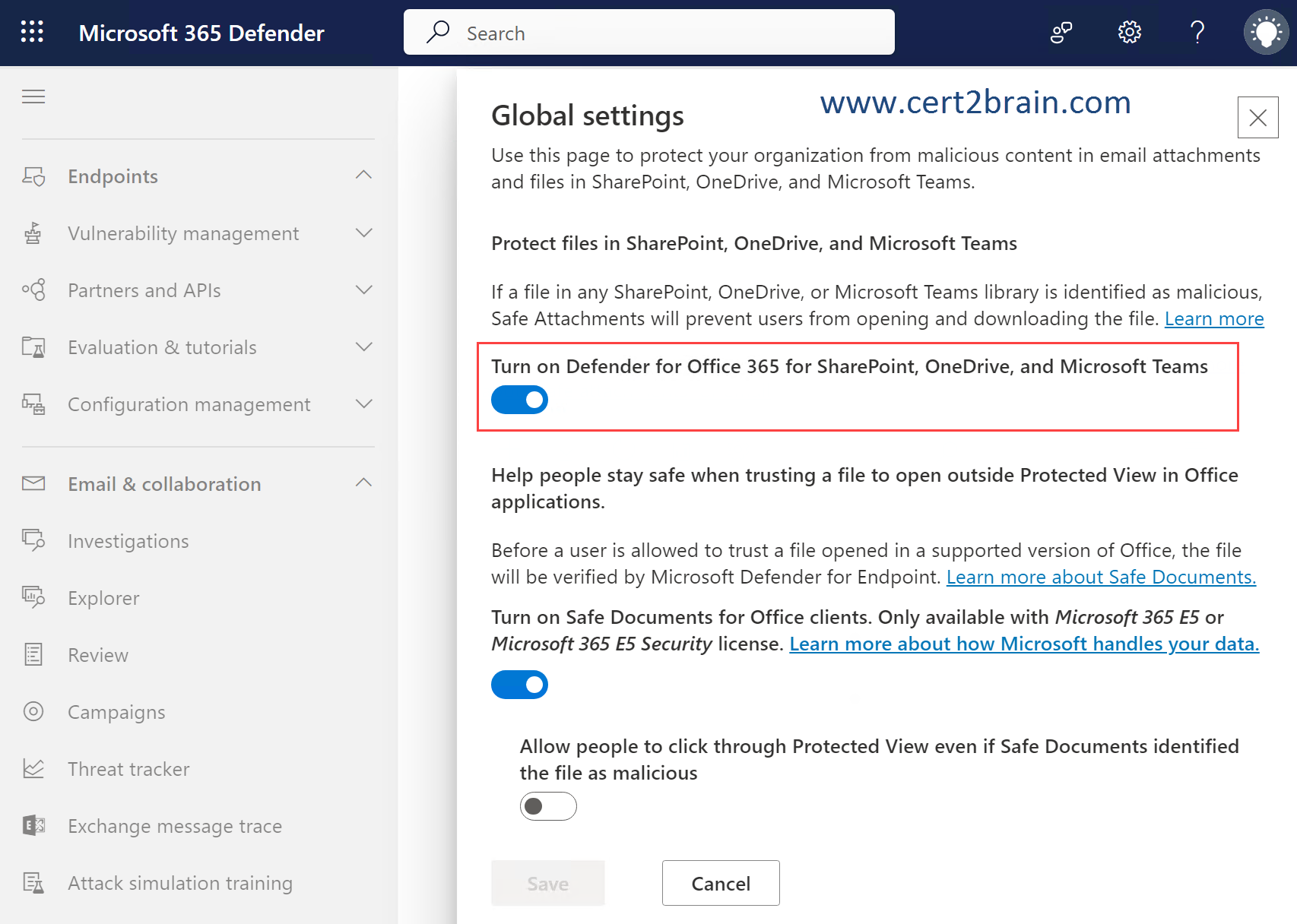
Reference: Turn on Safe Attachments for SharePoint, OneDrive, and Microsoft Teams
Question: 488
Measured Skill: Implement Modern Device Services (40-45%)
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that contains a user named User1 and the administrators shown in the following table.
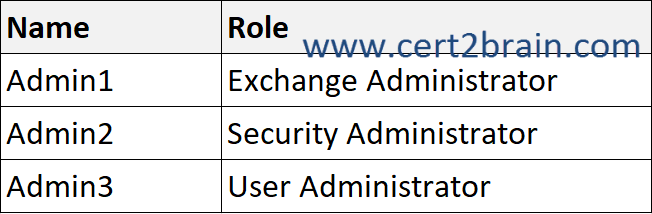
User1 reports that after sending 1,000 email messages in the morning, the user is blocked from sending additional emails.
You need to identify the following:
- Which administrators can unblock User1.
- What to configure to allow User1 to send at least 2,000 emails per day without being blocked.
What should you identify?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)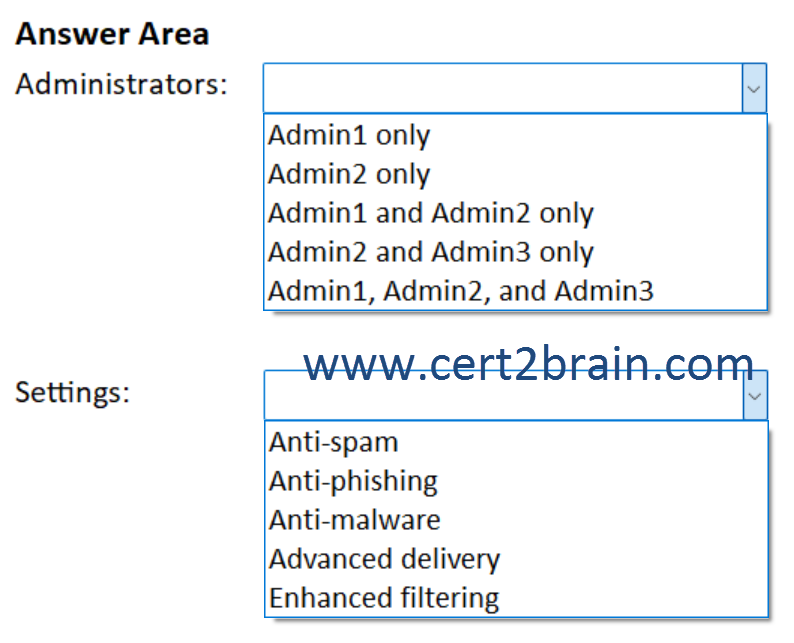
| A | Administrators: Admin1 only
Settings: Anti-malware |
| B | Administrators: Admin2 only
Settings: Anti-spam |
| C | Administrators: Admin1 and Admin2 only
Settings: Enhanced filtering |
| D | Administrators: Admin2 and Admin3 only
Settings: Anti-phishing |
| E | Administrators: Admin1, Admin2, and Admin3
Settings: Advanced delivery |
| F | Administrators: Admin1, Admin2, and Admin3
Settings: Anti-malware |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
In Microsoft 365 organizations with mailboxes in Exchange Online or standalone Exchange Online Protection (EOP) organizations without Exchange Online mailboxes, several things happen if a user exceeds the outbound sending limits of the service or the limits in outbound spam policies:
The user is restricted from sending email, but they can still receive email.
The user is added to the Restricted entities page in the Microsoft 365 Defender portal.
A restricted entity is a user account or a connector that's blocked from sending email due to indications of compromise, which typically includes exceeding message receiving and sending limits.
If the user tries to send email, the message is returned in a non-delivery report (also known as an NDR or bounce message) with the error code 5.1.8 and the following text:
"Your message couldn't be delivered because you weren't recognized as a valid sender. The most common reason for this is that your email address is suspected of sending spam and it's no longer allowed to send email. Contact your email admin for assistance. Remote Server returned '550 5.1.8 Access denied, bad outbound sender."
To unblock a user, you need to be assigned permissions before you can do the procedures in this article. You have the following options:
- Exchange Online RBAC:
- Remove user accounts from the Restricted entities page: Membership in the Organization Management or Security Administrator role groups.
- Read-only access to the Restricted entities page: Membership in the Global Reader, Security Reader, or View-Only Organization Management role groups.
- Azure AD RBAC: Membership in the Global Administrator, Security Administrator, Global Reader, or Security Reader roles gives users the required permissions and permissions for other features in Microsoft 365.
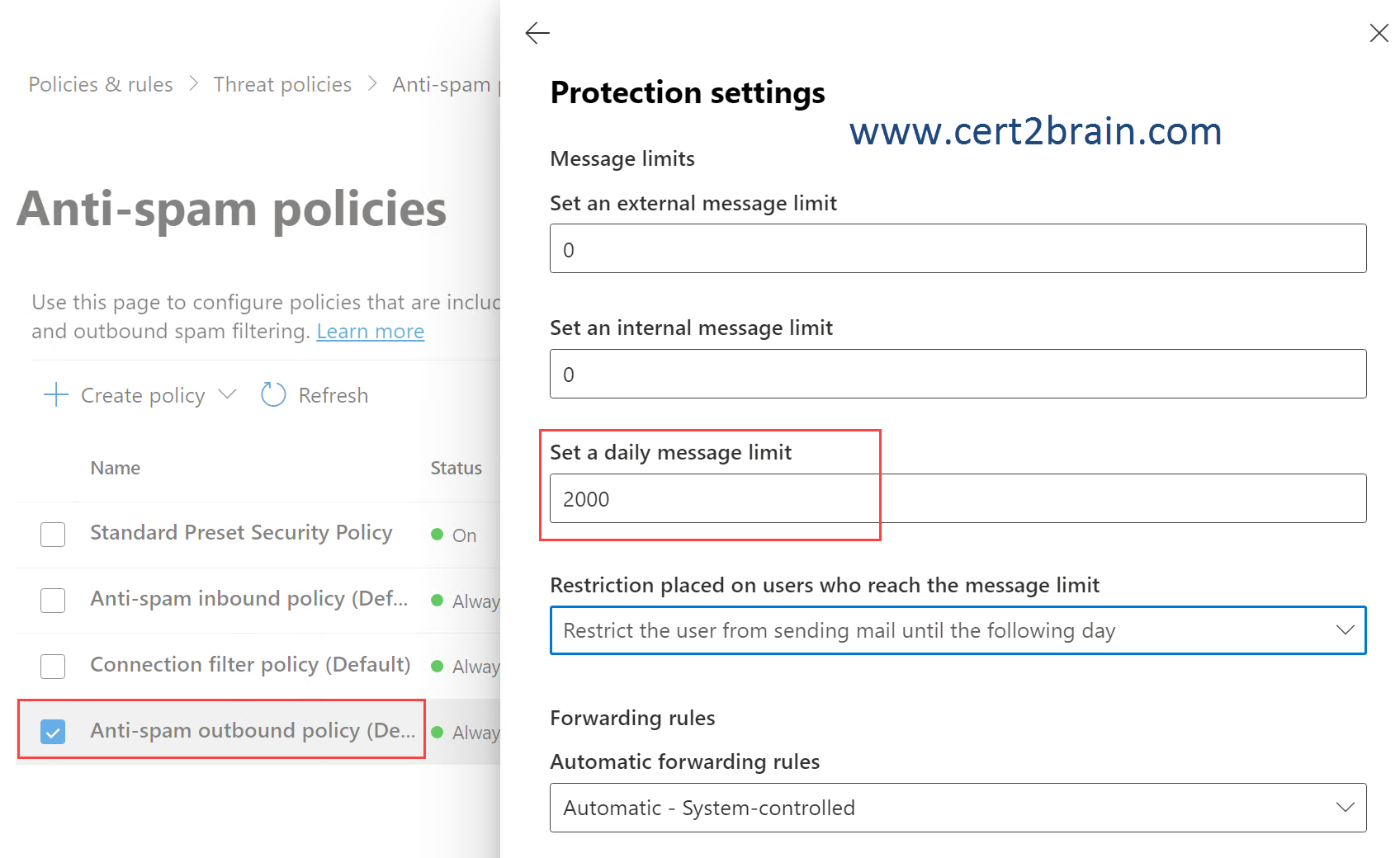
Note: The daily limit of 2000 cannot be saved because there is a limit of a maximum of 1000 outgoing mails per user per day at the tenant level. The limit of 1000 can be decreased but not increased for an individual user using the -RecipientLimits parameter of the Set-Mailbox PowerShell cmdlet.
References:
Remove blocked users from the Restricted entities page
Customizable Tenant-level Recipient Limits