Microsoft - SC-100: Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
Sample Questions
Question: 334
Measured Skill: Design security solutions for applications and data (20–25%)
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription.
Microsoft Purview is configured to protect data in only Microsoft Exchange Online and SharePoint Online. Custom sensitive information types (SITs) have been created to identify confidential data.
You discover that users access third-party generative AI websites from their Windows devices.
You need to recommend a solution to block AI prompts that contain confidential data and scan the AI prompts submitted to the third-party websites.
What should you recommend for each requirement?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)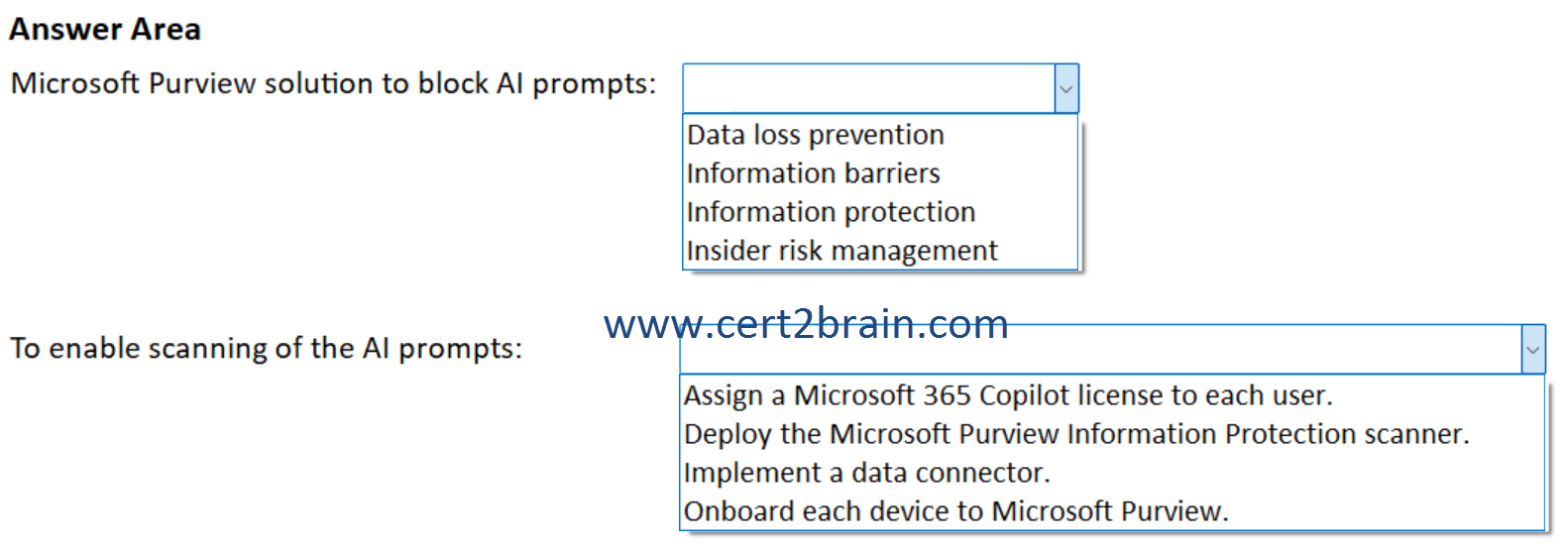
| A | Microsoft Purview solution to block AI prompts: Data loss prevention
To enable scanning of the AI prompts: Deploy the Microsoft Purview Information Protection scanner. |
| B | Microsoft Purview solution to block AI prompts: Data loss prevention
To enable scanning of the AI prompts: Onboard each device to Microsoft Purview. |
| C | Microsoft Purview solution to block AI prompts: Information barriers
To enable scanning of the AI prompts: Assign a Microsoft 365 Copilot license to each user. |
| D | Microsoft Purview solution to block AI prompts: Information protection
To enable scanning of the AI prompts: Implement a data connector. |
| E | Microsoft Purview solution to block AI prompts: Information protection
To enable scanning of the AI prompts: Onboard each device to Microsoft Purview. |
| F | Microsoft Purview solution to block AI prompts: Insider risk management
To enable scanning of the AI prompts: Assign a Microsoft 365 Copilot license to each user. |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention (DLP) helps you identify sensitive items across Microsoft 365 services and endpoints, monitor them, and helps protect against leakage of those items. It uses deep content inspection and contextual analysis to identify sensitive items and it enforces policies to protect sensitive data such as financial records, health information, or intellectual property.
Windows computers that are onboarded to Microsoft Purview can be configured for Endpoint data loss prevention (DLP) policies that warn or block users from sharing sensitive information with third-party generative AI sites that are accessed via a browser. For example, a user is prevented from pasting credit card numbers into ChatGPT, or they see a warning that they can override.
Reference: Microsoft Purview data security and compliance protections for generative AI apps
Question: 335
Measured Skill: Design security solutions for applications and data (20–25%)
Your company has offices in New York City and London. The London office contains an on- premises app named App1.
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant named contoso.com that is hosted in North America.
You plan to manage access to App1 for the users in the London office by using Microsoft Entra Private Access. You will deploy Private Access by performing the following actions in the London office:
- Deploy Microsoft Entra application proxy connectors.
- Provision an ExpressRoute circuit to the closest peering location.
You need to optimize the network for the planned deployment. The solution must meet the following requirements:
- Maximize redundancy for connectivity to App1.
- Minimize network latency when accessing App1.
- Maximize security.
- Minimize costs.
What should you include in the solution?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)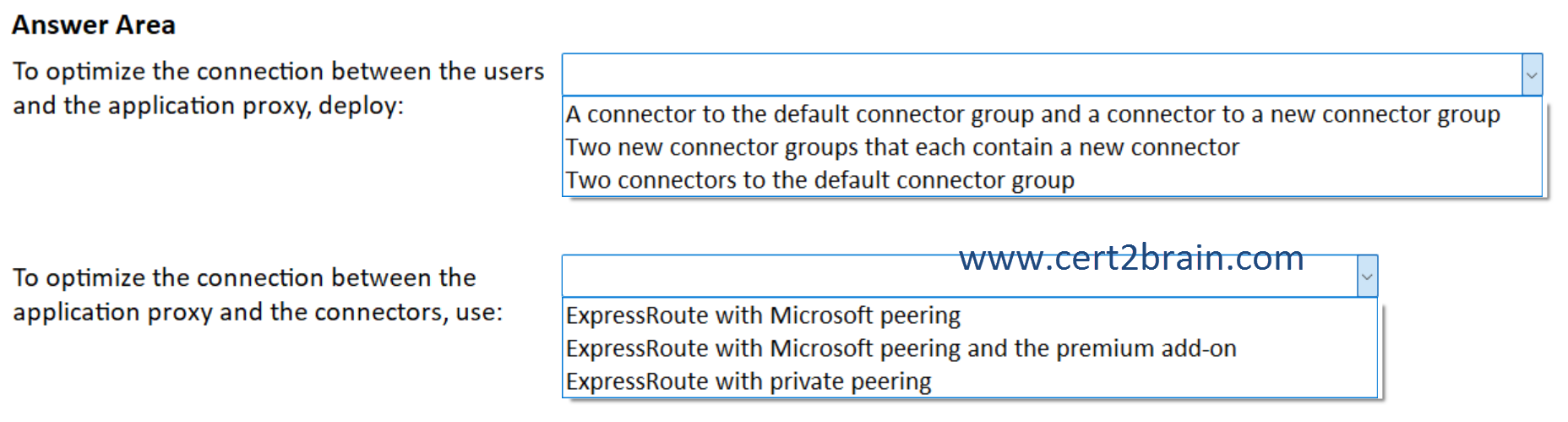
| A | To optimize the connection between the users and the application proxy, deploy: A connector to the default connector group and a connector to a new connector group
To optimize the connection between the application proxy and the connectors, use: ExpressRoute with Microsoft peering and the premium add-on |
| B | To optimize the connection between the users and the application proxy, deploy: A connector to the default connector group and a connector to a new connector group
To optimize the connection between the application proxy and the connectors, use: ExpressRoute with Microsoft peering |
| C | To optimize the connection between the users and the application proxy, deploy: Two new connector groups that each contain a new connector
To optimize the connection between the application proxy and the connectors, use: ExpressRoute with private peering |
| D | To optimize the connection between the users and the application proxy, deploy: Two new connector groups that each contain a new connector
To optimize the connection between the application proxy and the connectors, use: ExpressRoute with Microsoft peering |
| E | To optimize the connection between the users and the application proxy, deploy: Two connectors to the default connector group
To optimize the connection between the application proxy and the connectors, use: ExpressRoute with private peering |
| F | To optimize the connection between the users and the application proxy, deploy: Two connectors to the default connector group
To optimize the connection between the application proxy and the connectors, use: ExpressRoute with Microsoft peering and the premium add-on |
Correct answer: EExplanation:
Microsoft Entra application proxy provides secure remote access to on-premises web applications. After a single sign-on to Microsoft Entra ID, users can access both cloud and on-premises applications through an external URL or an internal application portal.
Connectors are lightweight agents that sit in a private network and facilitate the outbound connection to the Microsoft Entra Private Access and application proxy services. Connectors must be installed on a Windows Server that has access to the backend resources. You can organize connectors into connector groups, with each group handling traffic to specific resources.
It's recommended that you always deploy multiple connectors for redundancy and scale. The connectors, in conjunction with the service, take care of all the high availability tasks and can be added or removed dynamically. Each time a new request arrives it's routed to one of the connectors that is available.
Each private network connector is assigned to a connector group. Connectors in the same connector group act as a single unit for high availability and load balancing. You can create new groups, assign connectors to them in the Microsoft Entra admin center, then assign specific connectors to serve specific applications. It's recommended to have at least two connectors in each connector group for high availability.
ExpressRoute circuits connect your on-premises infrastructure to Microsoft through a connectivity provider.
An ExpressRoute circuit has two routing domains/peerings: Azure Private and Microsoft. Each peering is configured identically on a pair of routers for high availability. Azure services are categorized as Azure public and Azure private to represent the IP addressing schemes.
Azure private peering
Azure compute services, such as virtual machines (IaaS) and cloud services (PaaS), deployed within a virtual network can be connected through the private peering domain. This domain is considered a trusted extension of your core network into Microsoft Azure. You can set up bi-directional connectivity between your core network and Azure virtual networks (VNets), allowing you to connect to virtual machines and cloud services directly on their private IP addresses.
Application Proxy connectors establish private connectivity between your on-prem network and Microsoft’s service.
Microsoft peering
Connectivity to Microsoft online services (Microsoft 365, Azure PaaS services, and Microsoft PSTN services) occurs through Microsoft peering. This peering enables bi-directional connectivity between your WAN and Microsoft cloud services. You must connect to Microsoft cloud services over public IP addresses owned by you or your connectivity provider and adhere to all defined rules.
References:
Understand the Microsoft Entra private network connector
Using Microsoft Entra application proxy to publish on-premises apps for remote users
How to configure private network connectors for Microsoft Entra Private Access and Microsoft Entra application proxy
ExpressRoute circuits and peering
Question: 336
Measured Skill: Design solutions that align with security best practices and priorities (20–25%)
You are designing new Azure applications based on security best practices from the Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure. Each application will be deployed to a dedicated and secure environment that will contain isolated instances of the following key Azure security resources:
- Azure Key Vault
- Virtual networks
- An Azure subscription
- Azure Policy assignments
- Network security groups (NSGs)
- Role-based access control (RBAC) assignments
You need to recommend which type of environment and which module to use to deploy the applications. The solution must use infrastructure as code (IaC) to deploy each application environment.
What should you recommend?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)
| A | Environment type: Landing zone
Module: Azure Resource Manager (ARM) or Bicep |
| B | Environment type: Landing zone
Module: Bicep or Terraform |
| C | Environment type: Management group
Module: Azure Resource Manager (ARM) or Terraform |
| D | Environment type: Private cloud
Module: Azure Resource Manager (ARM) or Bicep |
| E | Environment type: Resource group
Module: Bicep or Terraform |
| F | Environment type: Resource group
Module: Azure Resource Manager (ARM) or Terraform |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
We should recommend an Azure landing zone. An Azure landing zone is the standardized and recommended approach for all organizations utilizing Azure. It provides a consistent way to set up and manage your Azure environment at scale. It ensures consistency across your organization by aligning with key requirements for security, compliance, and operational efficiency through platform and application landing zones.
In the Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF), a landing zone is specifically defined as a preconfigured Azure environment built using infrastructure as code (IaC) that includes governance, security, networking, and identity controls.
The Azure Landing Zones IaC Accelerator provides an automated approach to deploy and manage the platform landing zone. It uses Bicep or Terraform based on Azure Verified Modules (AVM). This tool streamlines the setup of a continuous delivery environment and supports Azure DevOps and GitHub for version control systems (VCS), deployment pipelines, and runners.
References:
What is an Azure landing zone?
Platform landing zone implementation options
Question: 337
Measured Skill: Design security operations, identity, and compliance capabilities (30–35%)
Your network contains an on-premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain named Domain1. Domain1 contains 10 domain controllers.
You have an Azure subscription named Sub1 that contains a Microsoft Sentinel workspace named WS1.
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that contains 5,000 users. Each user is assigned a Microsoft 365 E3 license.
You need to recommend a solution to ingest security logs from all the domain controllers into WS1. The solution must meet the following requirements:
- The cost of ingesting data into WS1 must be minimized.
- WS1 must ingest all the Windows Security event logs generated by the domain controllers.
- The solution must support the generation of approximately 350 MB of logs per day from each domain controller.
What should you recommend?| A | Upgrade the user licenses to Microsoft 365 E5. |
| B | Onboard each domain controller to Microsoft Defender for Servers Plan 2. |
| C | Configure Auxiliary logs in WS1. |
| D | Configure a volume cap for WS1. |
| E | Only ingest data from one domain controller into WS1. |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
The cost of ingesting data into WS1 must be minimized. We are going to ingest very large volumes of Windows Security logs: 10 DCs × 350 MB/day ˜ 3.5 GB/day. Standard analytics logs would be expensive.
In Microsoft Sentinel/Log Analytics auxiliary logs provide the lowest-cost ingestion tier. They are designed for high-volume logs, long retention, and basic querying only (not full analytics features).
References:
Plan costs and understand Microsoft Sentinel pricing and billing
Log retention tiers in Microsoft Sentinel
Set up a table with the Auxiliary plan in your Log Analytics workspace
Question: 338
Measured Skill: Design security solutions for applications and data (20–25%)
You have an Azure subscription.
You enable the Defender Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) plan.
You need to optimize the security posture of the subscription by implementing Microsoft Defender for Cloud secure score recommendations.
Which security policy should you enable, and which factors will have a direct impact on the secure score?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)
| A | Security policy: Azure CSPM
Factors: Built-in security policy recommendations only |
| B | Security policy: Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark
Factors: Built-in security policy recommendations only |
| C | Security policy: CIS Microsoft Azure Foundation Benchmark v1.4.0
Factors: Built-in security policy recommendations and risk priorization rankings only |
| D | Security policy: Azure CSPM
Factors: Built-in security policy recommendations and risk priorization rankings only |
| E | Security policy: CIS Microsoft Azure Foundation Benchmark v1.4.0
Factors: Built-in security policy recommendations, risk priorization rankings, and critical asset classifications |
| F | Security policy: Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark
Factors: Built-in security policy recommendations, risk priorization rankings, and critical asset classifications |
Correct answer: FExplanation:
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a core feature of Microsoft Defender for Cloud. CSPM provides continuous visibility into the security state of your cloud assets and workloads, offering actionable guidance to improve your security posture across Azure, AWS, and GCP.
Security policies in Microsoft Defender for Cloud define how your cloud resources are evaluated for security across Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). A policy specifies the standards, controls, and conditions Defender for Cloud uses to assess resource configurations and identify potential security risks.
Each policy includes security standards, which define the controls and assessment logic applied to your environment. Defender for Cloud continuously evaluates your resources against these standards. When a resource doesn’t meet a defined control, Defender for Cloud generates a security recommendation that describes the issue and the actions required to remediate it.
By default, when you enable Defender for Cloud on an Azure subscription, the Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark (MCSB) standard is enabled and provides recommendations to secure your multicloud environment. The secure score based on some of the MCSB recommendations helps you monitor cloud compliance. A higher score indicates a lower identified risk level.
The Cloud secure score is risk-based. It introduces asset risk factors and asset criticality into the calculation, making the score more?accurate?and enabling smarter prioritization of?high?risk?level recommendations than the previous classic secure score.?
References:
What is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Security policies in Defender for Cloud
Microsoft cloud security benchmark in Defender for Cloud
Secure score in Defender for Cloud