Microsoft - SC-200: Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
Sample Questions
Question: 425
Measured Skill: Manage a security operations environment (20–25%)
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription.
You need to configure Microsoft Sentinel to collect logs from Microsoft Entra.
Which two nodes should you use in the Microsoft Defender portal?
(To answer, select the appropriate nodes in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct answer is worth one point.)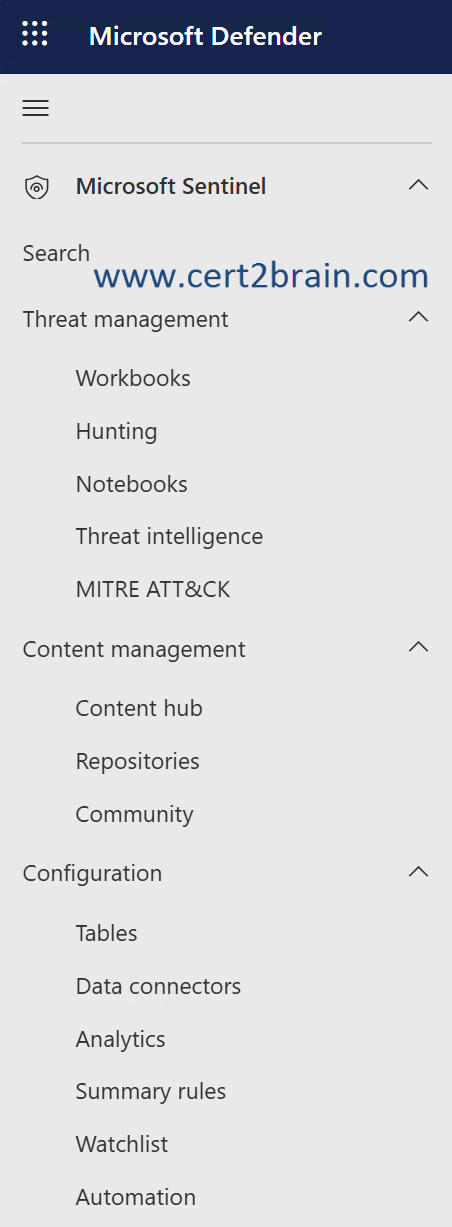
| A | Threat management - Threat intelligence |
| B | Content management - Content hub |
| C | Content management - Repositories |
| D | Configuration - Tables |
| E | Configuration - Data connectors |
| F | Configuration - Automation |
Correct answer: B, EExplanation:
Microsoft Entra ID logs provide comprehensive information about users, applications, and networks accessing your Microsoft Entra tenant. Microsoft Sentinel can collect these logs using the Microsoft Entra ID data connector.
As a prerequisite, we need to enable the Microsoft Entra ID data connector from Configuration - Data connectors.
To get prebuilt workbooks, analytics rules, playbooks, and more, we should also install the solution for Microsoft Entra ID from the Content Hub in Microsoft Sentinel.
References:
Send data to Microsoft Sentinel using the Microsoft Entra ID data connector
Connect data sources to Microsoft Sentinel by using data connectors
Question: 426
Measured Skill: Manage security threats (15–20%)
You have an Azure environment that contains 50 subscriptions, including a subscription named Sub1. Sub1 contains a Microsoft Sentinel workspace named Workspace1 that collects logs from the other subscriptions. Workspace1 contains a workbook named WB1.
To WB1, you add a parameters item named Item1. To Item1, you add a parameter named Parameter1.
You need to configure the drop-down menu for Parameter1 to meet the following requirements:
- Ensure that users can select one or more subscriptions to query.
- Provide users with a single option to query all the subscriptions.
The solution must minimize how long it takes to populate WB1 with data. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
What should you do?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)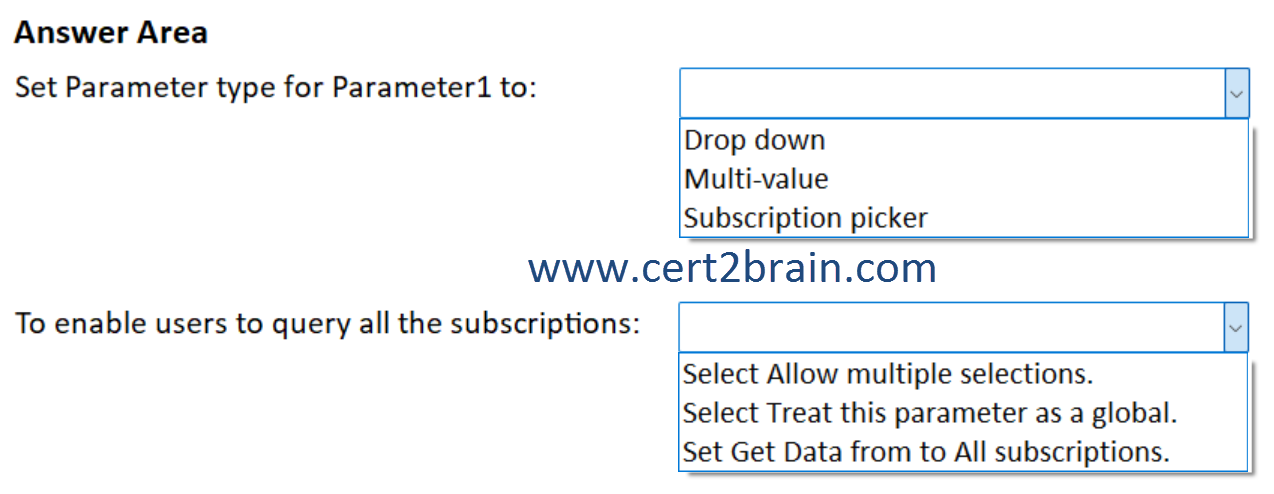
| A | Set Parameter type for Parameter1 to: Drop down
To enable users to query all the subscriptions: Select Treat this parameter as a global. |
| B | Set Parameter type for Parameter1 to: Drop down
To enable users to query all the subscriptions: Set Get Data from to All subscriptions. |
| C | Set Parameter type for Parameter1 to: Multi-value
To enable users to query all the subscriptions: Select Allow multiple selections. |
| D | Set Parameter type for Parameter1 to: Multi-value
To enable users to query all the subscriptions: Select Treat this parameter as a global. |
| E | Set Parameter type for Parameter1 to: Subscription picker
To enable users to query all the subscriptions: Select Allow multiple selections. |
| F | Set Parameter type for Parameter1 to: Subscription picker
To enable users to query all the subscriptions: Set Get Data from to All subscriptions. |
Correct answer: EExplanation:
The Parameter type should be set to Subscription picker. The Subscription picker type populates the drop down automatically with all available subscriptions.
To enable users to query all the subscriptions, we have to enable the Allow multiple selections option. Once the option is enabled, we get the Include in the drop down option which allows to add an item that selects all values at once.
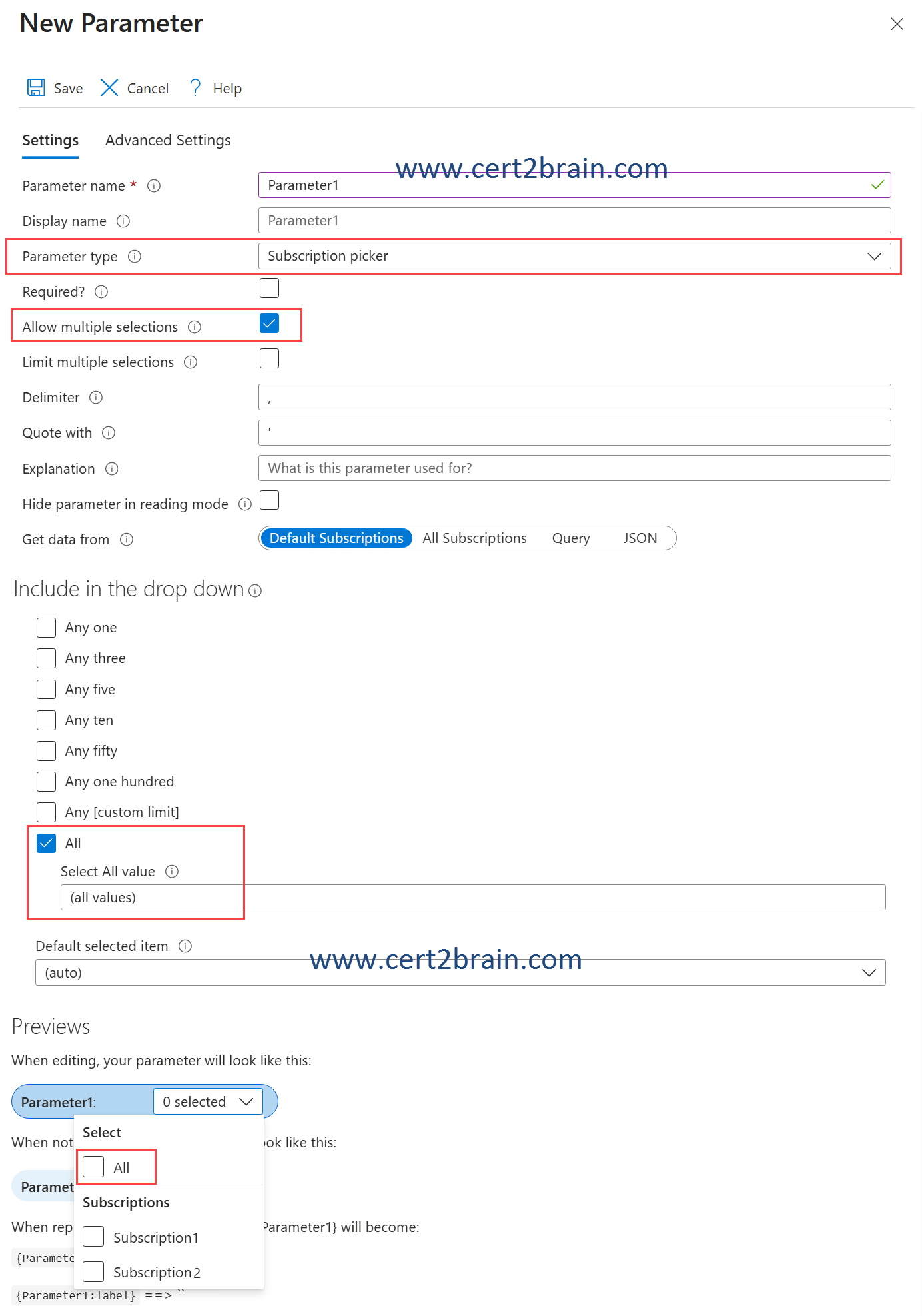
Reference: Azure Workbooks
Question: 427
Measured Skill: Manage a security operations environment (20–25%)
You have an on-premises virtual machine named VM1 that runs Windows Server.
You have a Microsoft Sentinel workspace named Workspace1.
You install the Azure Connected Machine agent on VM1.
You need to collect events from VM1 and send the events to Workspace1.
Which two actions should you perform?
(Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct answer is worth one point.)| A | OnVM1, install the Microsoft Monitoring Agent (MMA). |
| B | On VM1, install the Log Analytics agent. |
| C | From the Microsoft Defender portal, add the Windows Security Events via AMA data connector. |
| D | From the Microsoft Defender portal, add the Syslog via AMA data connector. |
| E | On VM1, enable the Azure Monitor Agent (AMA) extension. |
| F | From the Microsoft Defender portal, create a data collection rule (DCR) that targets VM1. |
Correct answer: E, FExplanation:
The Azure Connected Machine agent lets you manage Windows and Linux machines hosted outside of Azure, on your corporate network or other cloud providers.
The Azure Connected Machine agent package contains several logical components bundled together:
The Hybrid Instance Metadata service (HIMDS) manages the connection to Azure and the connected machine's Azure identity.
The machine configuration agent provides functionality such as assessing whether the machine complies with required policies and enforcing compliance.
The Extension agent manages VM extensions, including install, uninstall, and upgrade. Azure downloads extensions and copies them to the %SystemDrive%\%ProgramFiles%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\ExtensionService\downloads folder on Windows, and to /opt/GC_Ext/downloads on Linux. On Windows, the extension installs to the following path %SystemDrive%\Packages\Plugins\<extension>, and on Linux the extension installs to /var/lib/waagent/<extension>.
The Azure Monitor Agent (AMA) collects monitoring data from the guest operating system of Azure and hybrid virtual machines (VMs). It delivers the data to Azure Monitor for use by features, insights, and other services, such as Microsoft Sentinel and Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
The Azure Monitor Agent collects data according to data collection rules (DCRs) that are associated with the agent. DCRs define what data is collected, how it gets processed, and where it gets sent.
When the agent is installed, it retrieves and applies any DCRs that are associated with it and periodically checks for updates. It enables centralized and consistent configuration of data collection across multiple agents and environments.
The Azure Monitor Agent extension can be easily enabled using the Azure portal as shown below:
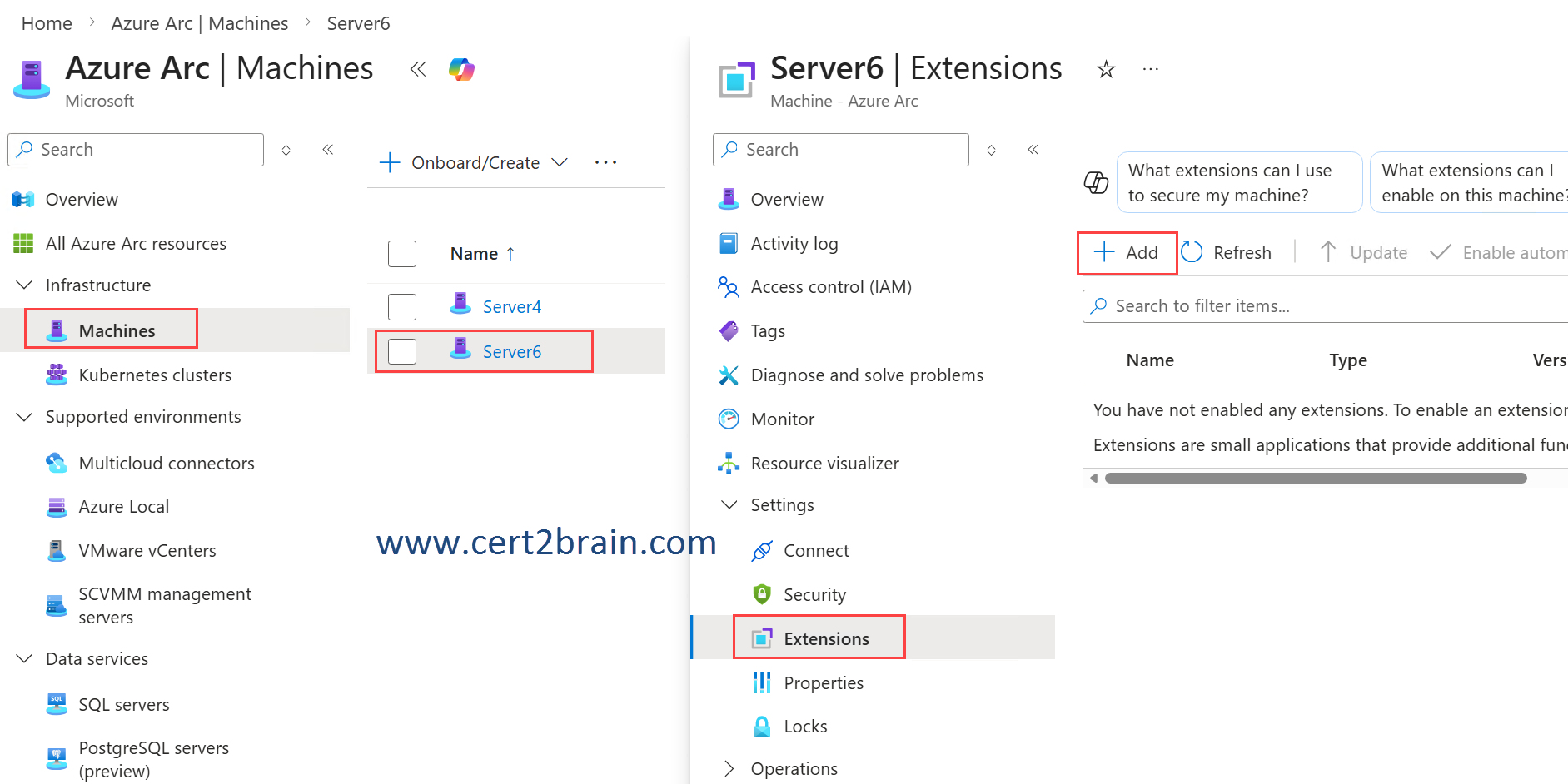
References:
Overview of Azure Connected Machine agent
Azure Monitor Agent overview
Question: 428
Measured Skill: Manage incident response (25–30%)
You have a Microsoft Sentinel workspace that contains the following tables.
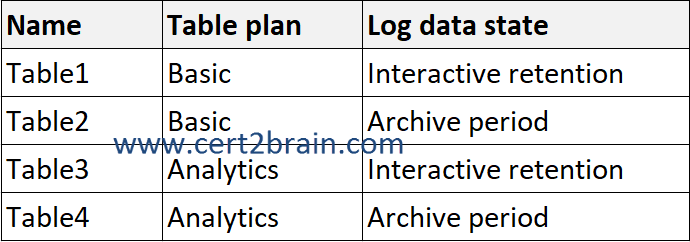
You need to investigate the log data by using a search.
Which tables can you search?| A | Table3 only |
| B | Table1 and Table3 only |
| C | Table3 and Table4 only |
| D | Table1, Table3, and Table4 only |
| E | Table1, Table2, Table3, and Table4 |
Correct answer: EExplanation:
Use a search job to retrieve data stored in long-term retention, or to scan through large volumes of data, if the log query time-out of 10 minutes isn't sufficient. A search job scans through up to a year of data in a table for specific events. The search job sends its results to a new Analytics table in the same workspace as the source data.
Go to Search in Microsoft Sentinel from the Azure portal or the Microsoft Defender portal to enter your search criteria. Depending on the size of the target dataset, search times vary. While most search jobs take a few minutes to complete, searches across massive data sets that run up to 24 hours are also supported.
Use search jobs to:
Retrieve records from long-term retention and tables with the Basic and Auxiliary plans into a new Analytics table where you can take advantage of Azure Monitor Log's full analytics capabilities.
Scan through large volumes of data, if the log query time-out of 10 minutes isn't sufficient.
References:
Search for specific events across large datasets in Microsoft Sentinel
Run search jobs in Azure Monitor
Question: 429
Measured Skill: Manage security threats (15–20%)
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that uses Microsoft Defender XDR and contains a user named User1.
You need to ensure that User1 can identify endpoint vulnerabilities on devices affected by a security incident. The solution must NOT require that User1 have KQL knowledge.
Which three actions should User1 perform in the Microsoft Defender portal in sequence?
(To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.)
| A | Sequence: 6, 5, 2 |
| B | Sequence: 4, 3, 2 |
| C | Sequence: 4, 1, 5 |
| D | Sequence: 6, 1, 2 |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
We should use the query builder in Microsoft Defender Advanced hunting.
Microsoft Defender Advanced hunting is a query-based threat hunting tool that you use to explore up to 30 days of raw data. You can proactively inspect events in your network to locate threat indicators and entities. The flexible access to data enables unconstrained hunting for both known and potential threats.
Advanced hunting supports two modes: guided and advanced. The query builder in guided mode allows analysts to craft meaningful hunting queries without knowing Kusto Query Language (KQL) or the data schema. Analysts from every tier of experience can use the query builder to filter through data from the last 30 days to look for threats, expand incident investigations, perform data analytics on threat data, or focus on specific threat areas.
References:
Proactively hunt for threats with advanced hunting in Microsoft Defender
Build hunting queries using guided mode in Microsoft Defender