Microsoft - SC-300: Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
Sample Questions
Question: 412
Measured Skill: Implement authentication and access management (25–30%)
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription.
You create an access review named Review1. Review1 requires that every six months, Microsoft 365 group owners review guest user access to their groups.
You need to ensure that if the group owners fail to review the membership of Review1, guest users are removed automatically.
Which settings should you configure for Review1?| A | Reviewers |
| B | General |
| C | Advanced settings |
| D | Upon completion settings |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
To ensure that if the group owners fail to review the membership of Review1, guest users are removed automatically, we need to configure the Upon completion settings as shown below.
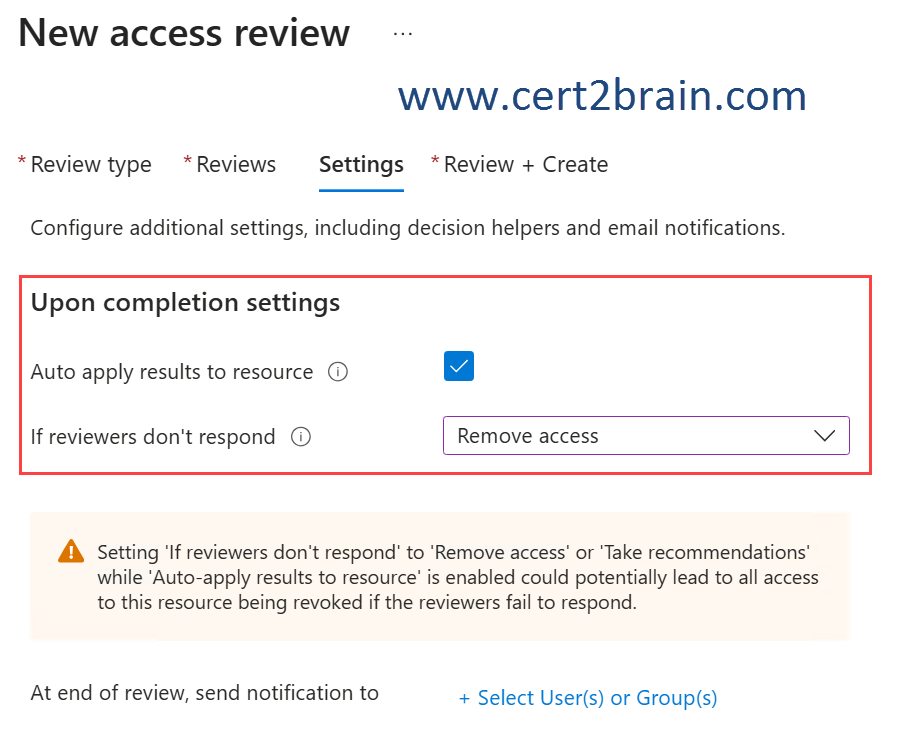
Reference: Manage guest access with access reviews
Question: 413
Measured Skill: Implement authentication and access management (25–30%)
You have an Azure subscription that contains a group named Group1 and two users named User1 and User2. User1 is a member of Group1.
You register an enterprise application named App1.
You enable self-service application access for App1 and configure the following settings:
- Allow users to request access to this application: Yes
- To which group should assigned users be added: Group1
- Require approval before granting access to this application: Yes
- Who is allowed to approve access to this application: User2
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
(NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)
| A | User1 must request access to App1 before they can use the app: Yes
If User2 requests access to App1, they will be added to Group1 automatically: Yes
User2 can approve App1 requests by using the Microsoft Entra admin center: Yes |
| B | User1 must request access to App1 before they can use the app: Yes
If User2 requests access to App1, they will be added to Group1 automatically: Yes
User2 can approve App1 requests by using the Microsoft Entra admin center: No |
| C | User1 must request access to App1 before they can use the app: Yes
If User2 requests access to App1, they will be added to Group1 automatically: No
User2 can approve App1 requests by using the Microsoft Entra admin center: No |
| D | User1 must request access to App1 before they can use the app: No
If User2 requests access to App1, they will be added to Group1 automatically: Yes
User2 can approve App1 requests by using the Microsoft Entra admin center: Yes |
| E | User1 must request access to App1 before they can use the app: No
If User2 requests access to App1, they will be added to Group1 automatically: No
User2 can approve App1 requests by using the Microsoft Entra admin center: Yes |
| F | User1 must request access to App1 before they can use the app: No
If User2 requests access to App1, they will be added to Group1 automatically: No
User2 can approve App1 requests by using the Microsoft Entra admin center: No |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
Self-service application access is a great way to allow users to self-discover applications, and optionally allow the business group to approve access to those applications.
If you set Allow users to request access to this application to Yes, all users will be allowed to view and request access to use the application when they click "Add App" in My Apps.
Once a user has requested access to the application and that request has been approved, they will be added to the group you select for the To which group should assigned users be added setting.
You can enable an email notifying approvers when a user requests access to an application that requires their approval. You can select up to ten individual business approvers. If you specify multiple approvers, any single approver can approve an access request in their My Apps portal. Groups aren't supported.
Reference: Enable self-service application assignment
Question: 414
Measured Skill: Implement and manage user identities (20–25%)
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant named contoso.com that has the default cross-tenant access settings configured as shown in the following table.
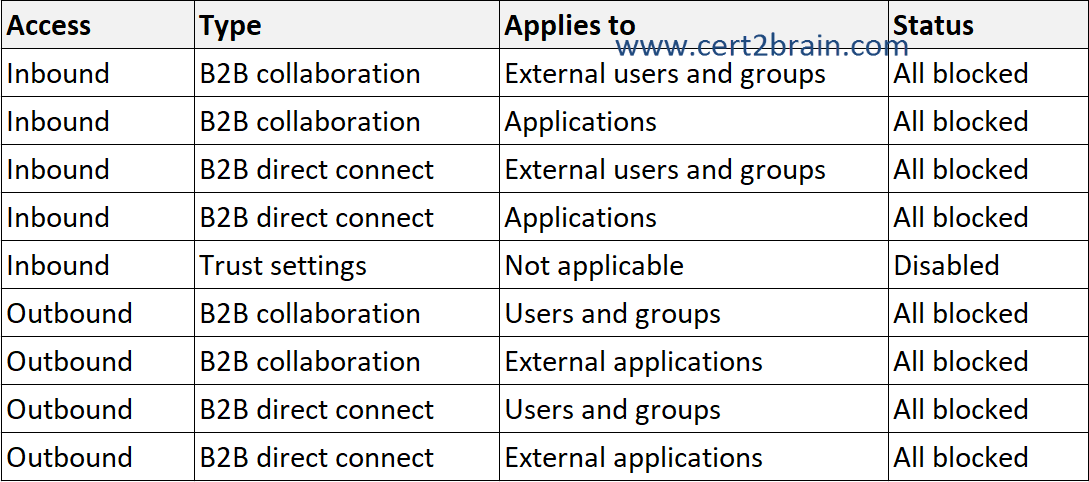
You have two partner organizations named Fabrikam, Inc. and A. Datum Corporation. Fabrikam has a Microsoft 365 domain named fabrikam.com. A. Datum has a Microsoft 365 domain named adatum.com.
You configure cross-tenant access for fabrikam.com as shown in the following table.
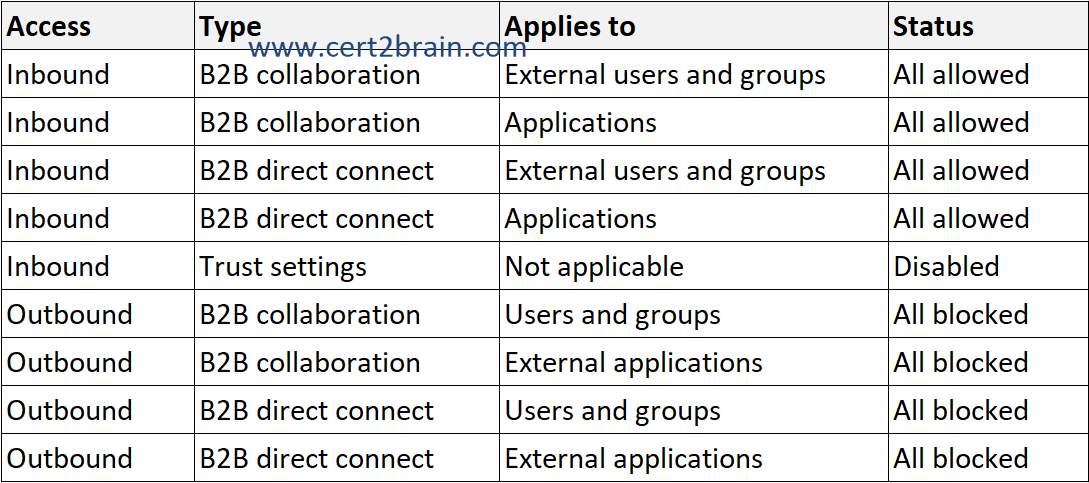
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
(NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)
| A | A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: Yes
A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@adatum.com: Yes
A user in contoso.com can accept a guest invitation from a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: Yes |
| B | A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: Yes
A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@adatum.com: Yes
A user in contoso.com can accept a guest invitation from a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: No |
| C | A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: Yes
A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@adatum.com: No
A user in contoso.com can accept a guest invitation from a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: Yes |
| D | A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: No
A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@adatum.com: Yes
A user in contoso.com can accept a guest invitation from a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: No |
| E | A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: No
A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@adatum.com: No
A user in contoso.com can accept a guest invitation from a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: Yes |
| F | A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: No
A user in contoso.com can send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@adatum.com: No
A user in contoso.com can accept a guest invitation from a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com: No |
Correct answer: EExplanation:
Microsoft Entra organizations can use External ID cross-tenant access settings to manage collaboration with other Microsoft Entra organizations and Microsoft Azure clouds through B2B collaboration and B2B direct connect. The cross-tenant access settings provide granular control over inbound and outbound access, allowing you to trust multifactor authentication (MFA) and device claims from other organizations.
Default settings (B2B collaboration and B2B direct connect) apply to all external Microsoft Entra tenants not listed on the organizational settings tab. These default settings can be modified but not deleted.
Here the default settings apply to the users in adatum.com while the fabrikam.com has their own organizational settings applied.
When using B2B Collaboration, you invite external users from another Microsoft Entra tenant. Those users become guest accounts (UserType = Guest) in your directory. They authenticate in their home tenant, but access resources in your tenant.
When using B2B Diret Connect, employees from another Entra tenant accessing your apps directly, without being added as guests.
By default, B2B collaboration with other Microsoft Entra organizations is enabled, and B2B direct connect is blocked. But the following comprehensive admin settings let you manage both of these features.
Outbound access settings control whether your users can access resources in an external organization. You can apply these settings to everyone, or specify individual users, groups, and applications.
Inbound access settings control whether users from external Microsoft Entra organizations can access resources in your organization. You can apply these settings to everyone, or specify individual users, groups, and applications.
Trust settings (inbound) determine whether your Conditional Access policies trust the multifactor authentication (MFA), compliant device, and Microsoft Entra hybrid joined device claims from an external organization if their users already satisfied these requirements in their home tenants. For example, when you configure your trust settings to trust MFA, your MFA policies are still applied to external users, but users who already completed MFA in their home tenants don't have to complete MFA again in your tenant.
All outbound B2B collaboration settings for fabrikam.com are blocked. A user in contoso.com can't send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@fabrikam.com. Inbound B2B collaboration are allowed. This means, a user from fabrikam.com could invite a user from contoso.com as a guest user.
All outbound B2B collaboration settings for adatum.com are blocked. A user in contoso.com can't send a guest invitation to a user that has an email address of user1@adatum.com.
References:
Overview: Cross-tenant access with Microsoft Entra External ID
Manage cross-tenant access settings for B2B collaboration
Set up B2B direct connect with an external organization
Question: 415
Measured Skill: Implement authentication and access management (25–30%)
You have an Azure subscription that contains a user named User1 and an Azure key vault named Vault1.
You need to ensure that User1 can read the metadata of certificates, keys, and secrets stored in Vault1. The solution must follow the principle of least privilege.
Which role should you assign to User1?| A | Key Vault Secrets User |
| B | Key Vault Crypto User |
| C | Key Vault Reader |
| D | Key Vault Crypto Officer |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
The Key Vault Reader role is the minimum user role required to read the metadata of certificates, keys, and secrets stored in an Azure Key Vault. This role allows users to view the properties and attributes of these objects, but not to access their actual contents.
Azure built-in roles for Key Vault data plane operations
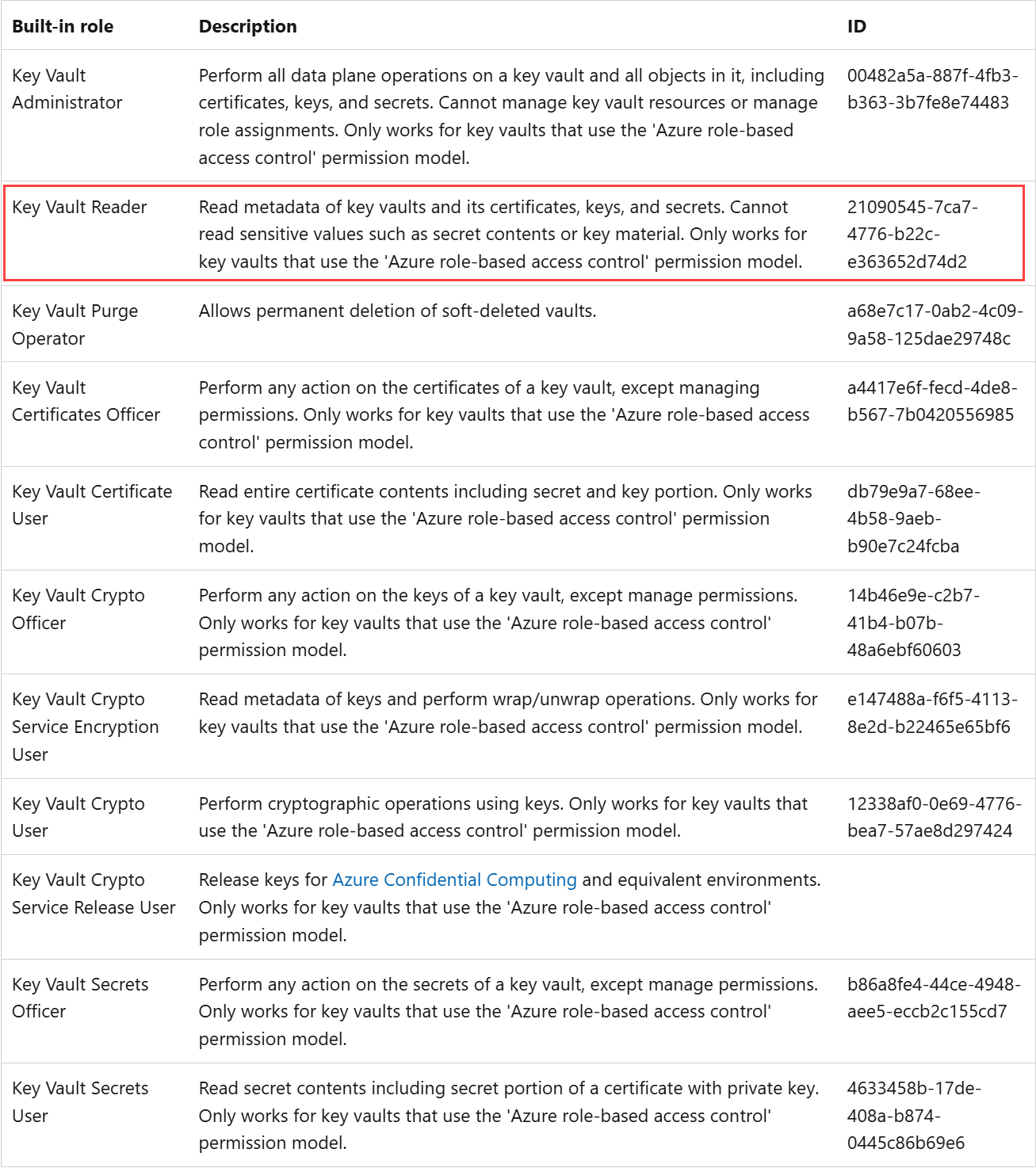
Reference: Provide access to Key Vault keys, certificates, and secrets with Azure role-based access control
Question: 416
Measured Skill: Plan and implement workload identities (20–25%)
You have an on-premises server named Server1 that runs Windows Server.
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant that contains an app registration named App1. App1 has Microsoft Graph application permissions.
You need to configure the environment to support App1. The solution must meet the following requirements:
- App1 must be accessible only from the corporate network.
- The credentials for App1 must NOT be stored as plain text.
- Non-interactive scheduled tasks on Server1 must be able to authenticate to App1.
What should you do?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)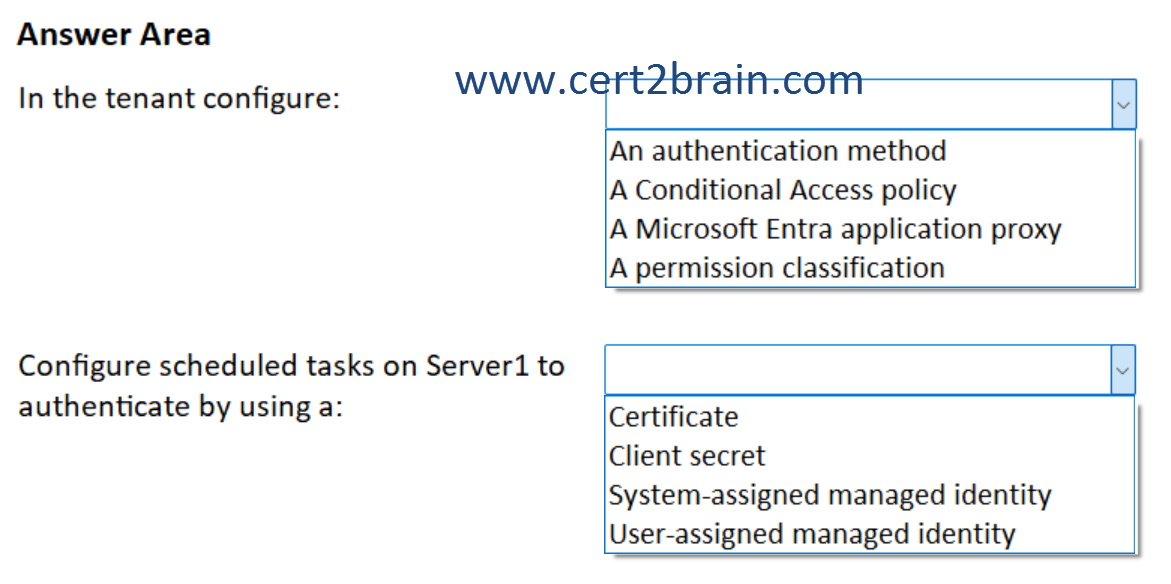
| A | In the tenant configure: An authentication method
Configure scheduled tasks on Server1 to authenticate by using a: System-assigned managed identity |
| B | In the tenant configure: A Conditional Access policy
Configure scheduled tasks on Server1 to authenticate by using a: Certificate |
| C | In the tenant configure: A Conditional Access policy
Configure scheduled tasks on Server1 to authenticate by using a: User-assigned managed identity |
| D | In the tenant configure: A Microsoft Entra application proxy
Configure scheduled tasks on Server1 to authenticate by using a: Client secret |
| E | In the tenant configure: A Microsoft Entra application proxy
Configure scheduled tasks on Server1 to authenticate by using a: Certificate |
| F | In the tenant configure: A permission classification
Configure scheduled tasks on Server1 to authenticate by using a: User-assigned managed identity |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
To restrict access to App1 to be accessible only from the corporate network, we should implement a Conditional Access policy, that has App1 defined as the Target resource and the corporate network as a Locations condition.
To enable non-interactive scheduled tasks on Server1 to authenticate to App1, we should use a certificate. A certificate meets the requirement that credentials for App1 must NOT be stored as plain text.
Windows Task Scheduler can run a script or executable that performs certificate-based authentication, as long as the script or app uses the certificate programmatically to get a token from Microsoft Entra ID. Windows Task Scheduler itself can't handle the certificate login.
Example:
$tenantId = "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
$clientId = "yyyyyyyy-yyyy-yyyy-yyyy-yyyyyyyyyyyy"
$certThumbprint = "ABC123DEF456..." # certificate thumbprint
$cert = Get-Item "Cert:\CurrentUser\My\$certThumbprint"
$token = Get-MsalToken -ClientId $clientId -TenantId $tenantId -ClientCertificate $cert -Scopes "https://graph.microsoft.com/.default"
Note: Managed identities in Azure can be used with Azure resources only. They can't be used by tasks or resources hosted on-premises.
References:
Use Get-MSALtoken to Connect to MS Graph
Connect to Microsoft Graph Using Get-MsalToken