Microsoft - SC-401: Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
Sample Questions
Question: 259
Measured Skill: Implement data loss prevention and retention (30–35%)
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that contains the users shown in the following table.
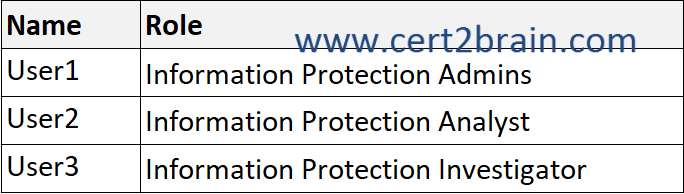
You need to delegate the following tasks:
- Create and manage data loss prevention (DLP) policies.
- Review classified content by using Content explorer.
The solution must use the principle of least privilege.
Which user should perform each task?
(To answer, select the appropriate options from each list in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.) 
| A | Create and manage data loss prevention (DLP) policies: User1
Review classified content by using Content explorer: User2 |
| B | Create and manage data loss prevention (DLP) policies: User1
Review classified content by using Content explorer: User3 |
| C | Create and manage data loss prevention (DLP) policies: User2
Review classified content by using Content explorer: User1 |
| D | Create and manage data loss prevention (DLP) policies: User2
Review classified content by using Content explorer: User3 |
| E | Create and manage data loss prevention (DLP) policies: User3
Review classified content by using Content explorer: User1 |
| F | Create and manage data loss prevention (DLP) policies: User3
Review classified content by using Content explorer: User2 |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
The table below lists the three role groups and the roles that are assigned to the role groups by default.

Reference: Roles and role groups in Microsoft Defender for Office 365 and Microsoft Purview
Question: 260
Measured Skill: Implement data loss prevention and retention (30–35%)
You have a Microsoft SharePoint Online site named Site1 that contains the users shown in following table.
You create the retention labels shown in the following table.

You publish the retention labels to Site1.
Site1 contains the files shown in following table.

Which files can User1 delete on May 15, 2025, and which files can User2 delete on August 15, 2025?
(To answer, select the appropriate options from each list in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.) 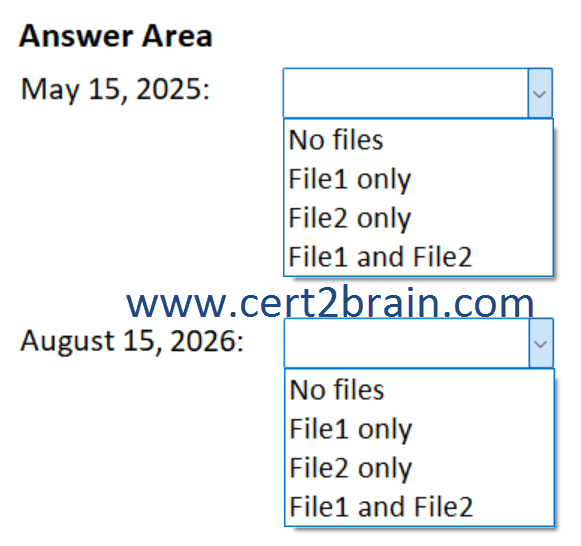
| A | May 15, 2025: No files
August 15, 2026: File1 only |
| B | May 15, 2025: No files
August 15, 2026: No files |
| C | May 15, 2025: File1 only
August 15, 2026: File1 and File2 |
| D | May 15, 2025: File2 only
August 15, 2026: File2 only |
| E | May 15, 2025: File1 and File2
August 15, 2026: No files |
| F | May 15, 2025: File1 and File2
August 15, 2026: File1 and File2 |
Correct answer: FExplanation:
Retention labels don't prevent users from deleting files from their original source location, but retention ensures items are retained in a special location if they were deleted.
When content has retention settings assigned to it, that content remains in its original location. Most of the time, people continue to work with their documents or mail as if nothing's changed. But if they edit or delete content that's included in the retention policy, a copy of the content is automatically retained.
For SharePoint and OneDrive sites: The copy is retained in the Preservation Hold library.
For Exchange mailboxes: The copy is retained in the Recoverable Items folder.
For Teams, Viva Engage messages, and interactions with Microosft 365 Copilot and Microsoft Copilot: The copy is retained in a hidden folder named SubstrateHolds as a subfolder in the Exchange Recoverable Items folder.
Reference: Learn about retention policies and retention labels
Question: 261
Measured Skill: Implement data loss prevention and retention (30–35%)
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 tenant that contains the users shown in the following table.

You have a retention policy that has the following configurations:
- Name: Policy1
- Retain items for a specific period: 5 years
- Locations to apply the policy: Exchange email, SharePoint sites
You place a Preservation Lock on Policy1.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
(NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.) 
| A | User1 can remove Exchange email from the locations: Yes
User2 can increase the retention period to seven years: Yes
User1 can decrease the retention period to three years: Yes |
| B | User1 can remove Exchange email from the locations: Yes
User2 can increase the retention period to seven years: Yes
User1 can decrease the retention period to three years: No |
| C | User1 can remove Exchange email from the locations: Yes
User2 can increase the retention period to seven years: No
User1 can decrease the retention period to three years: Yes |
| D | User1 can remove Exchange email from the locations: No
User2 can increase the retention period to seven years: Yes
User1 can decrease the retention period to three years: No |
| E | User1 can remove Exchange email from the locations: No
User2 can increase the retention period to seven years: No
User1 can decrease the retention period to three years: Yes |
| F | User1 can remove Exchange email from the locations: No
User2 can increase the retention period to seven years: No
User1 can decrease the retention period to three years: No |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
Preservation Lock locks a retention policy or retention label policy so that no one—including a global admin—can turn off the policy, delete the policy, or make it less restrictive. This configuration might be needed for regulatory requirements and can help safeguard against rogue administrators.
When a retention policy is locked:
- No one can disable the policy or delete it
- Locations can be added but not removed
- You can extend the retention period but not decrease it
When a retention label policy is locked:
- No one can disable the policy or delete it
- Locations can be added but not removed
- Labels can be added but not removed
In summary, a locked policy can be increased or extended, but it can't be reduced or turned off.
Reference: Use Preservation Lock to restrict changes to retention policies and retention label policies
Question: 262
Measured Skill: Implement data loss prevention and retention (30–35%)
You create a retention policy as shown in the following exhibit.
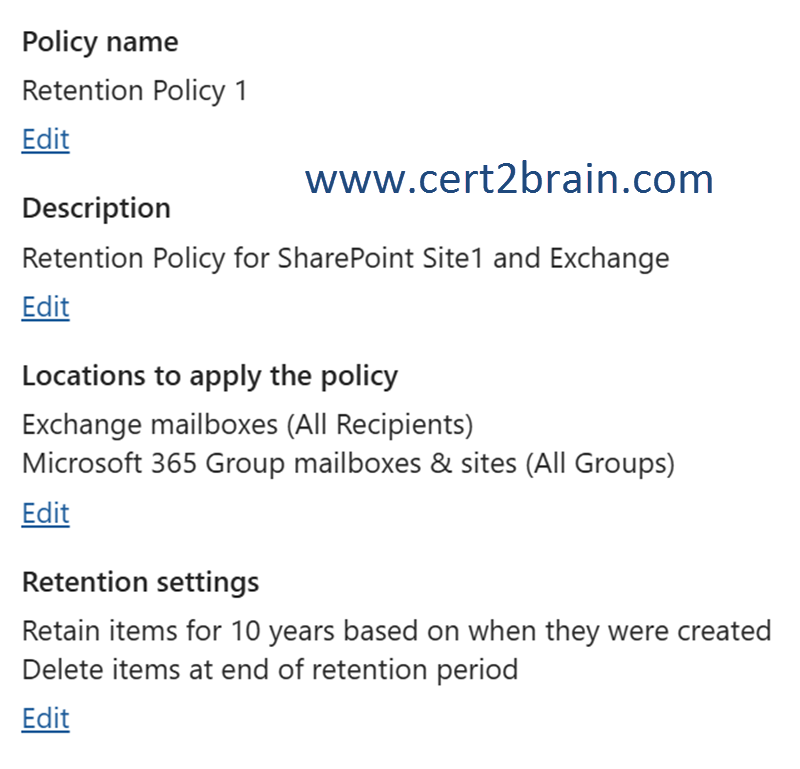
A user named User1 deletes a file named File1.docx from a Microsoft SharePoint Online site named Site1.
A user named User2 deletes an email and empties the Deleted Items folder in Microsoft Outlook.
Where is the content retained one year after deletion?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)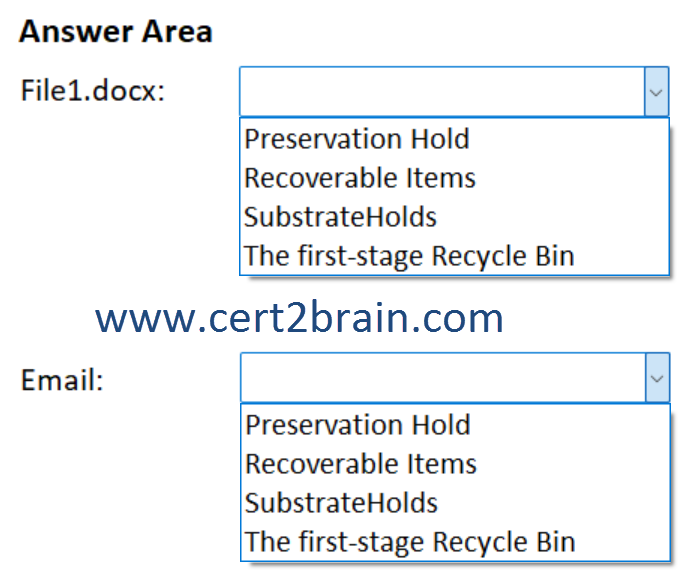
| A | File1.docx: Preservation Hold
Email: The first-stage Recycle Bin |
| B | File1.docx: Preservation Hold
Email: Recoverable Items |
| C | File1.docx: Recoverable Items
Email: Preservation Hold |
| D | File1.docx: SubstrateHolds
Email: Recoverable Items |
| E | File1.docx: The first-stage Recycle Bin
Email: SubstrateHolds |
| F | File1.docx: The first-stage Recycle Bin
Email: The first-stage Recycle Bin |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
When content has retention settings assigned to it, that content remains in its original location. Most of the time, people continue to work with their documents or mail as if nothing's changed. But if they edit or delete content that's included in the retention policy, a copy of the content is automatically retained.
For SharePoint and OneDrive sites: The copy is retained in the Preservation Hold library.
For Exchange mailboxes: The copy is retained in the Recoverable Items folder.
For Teams, Viva Engage messages, and interactions with Microsoft Copilot for Microsoft 365: The copy is retained in a hidden folder named SubstrateHolds as a subfolder in the Exchange Recoverable Items folder.
These secure locations and the retained content aren't visible to most people. In most cases, people don't even need to know that their content is subject to retention settings.
Reference: Learn about retention policies and retention labels
Question: 263
Measured Skill: Implement data loss prevention and retention (30–35%)
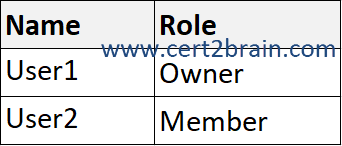
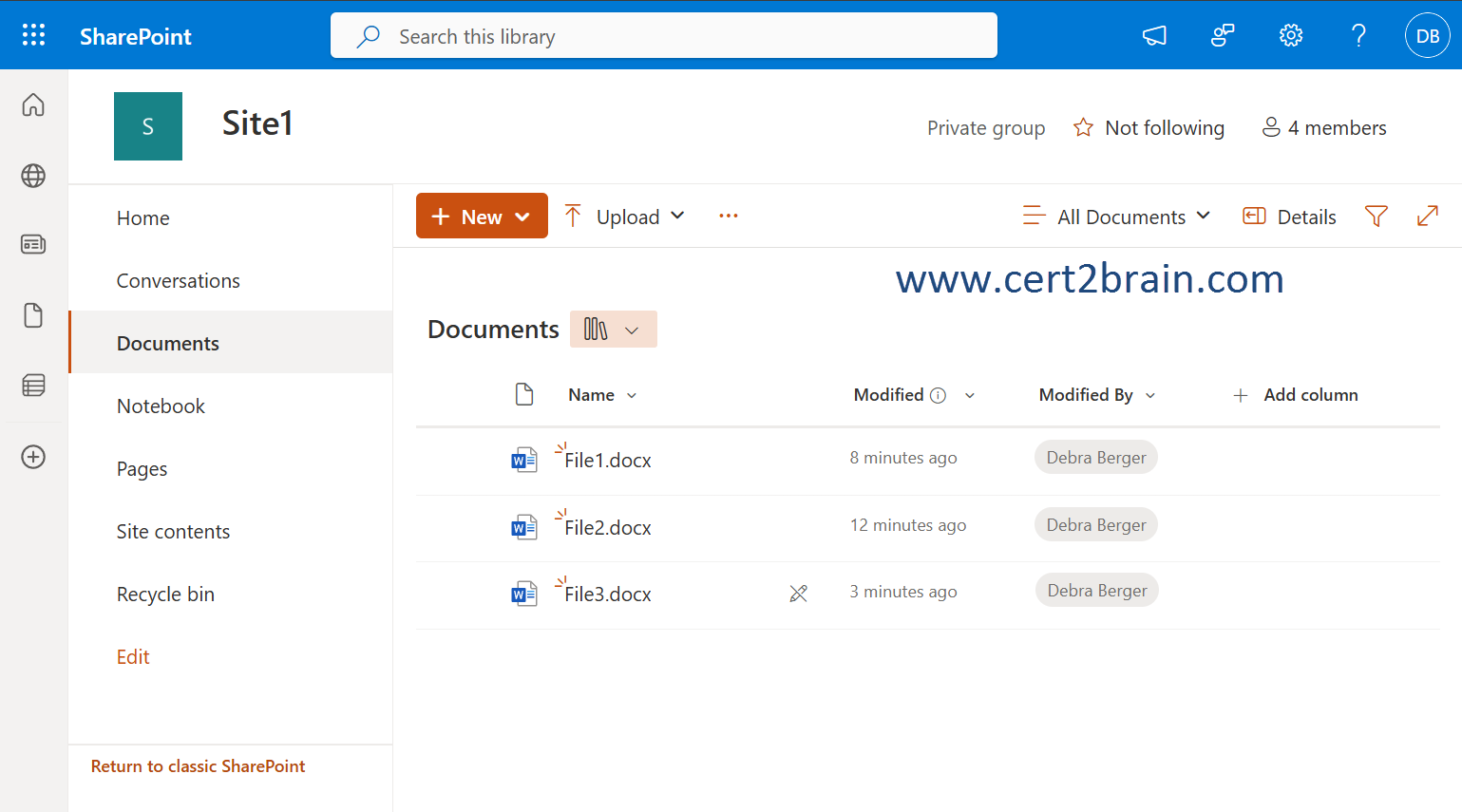
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 tenant that contains two users named User1 and User2 and a Microsoft SharePoint Online site named Site1 as shown in the following exhibit.
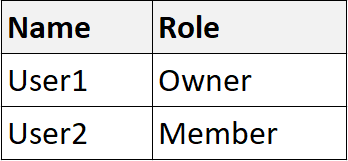
For Site1, the users are assigned the roles shown in the following table.
You publish a retention label named Retention1 to Site1.
To which files can the users apply Retention1?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)
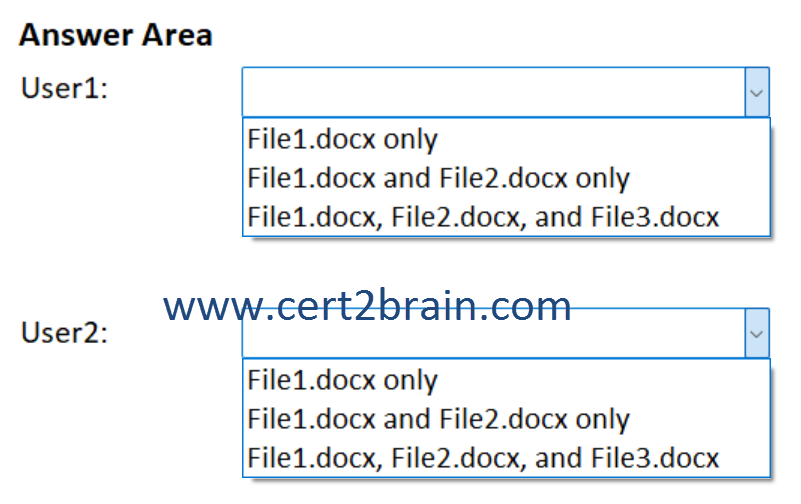
| A | User1: File1.docx only
User2: File1.docx only |
| B | User1: File1.docx only
User2: File1.docx, File2.docx, and File3.docx |
| C | User1: File1.docx and File2.docx only
User2: File1.docx and File2.docx only |
| D | User1: File1.docx and File2.docx only
User2: File1.docx only |
| E | User1: File1.docx, File2.docx, and File3.docx
User2: File1.docx and File2.docx only |
| F | User1: File1.docx, File2.docx, and File3.docx
User2: File1.docx, File2.docx, and File3.docx |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
In OneDrive or a SharePoint library, you can apply a retention label to a file, for example a Microsoft 365 document created in Word, PowerPoint, Excel, or a OneNote notebook. You can also label non-Office files, for example a PDF document or an image file. SharePointlist itemscan also be labeled.
You can also apply a label to a library or folder. When you label a library or folder, that retention label is applied by default to unlabeled files in that folder.
Both users (owner and member) can apply retention labels to all files in Site1. But, File3.docx has a read-only icon, which signals the file can't be modified.
References:
Publish retention labels and apply them in apps
Apply retention labels to files in SharePoint or OneDrive