Microsoft - SC-900: Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
Sample Questions
Question: 240
Measured Skill: Describe the capabilities of Microsoft security solutions (35–40%)
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.
| A | Microsoft Defender for Cloud plans can be enabled from the Azure portal. |
| B | Microsoft Defender for Cloud plans can be enabled from the Microsoft 365 admin center. |
| C | Microsoft Defender for Cloud plans can be enabled from the Microsoft Defender portal. |
| D | Microsoft Defender for Cloud plans can be enabled from the Microsoft Entra admin center. |
Correct answer: AExplanation:
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP), which is a unified solution that combines multiple cloud security tools to protect applications across their entire lifecycle. The solution provides a comprehensive view of your security posture across your cloud and on-premises resources. It also helps you secure multicloud and hybrid environments and integrates security into DevOps workflows.
After the Defender for Cloud solution is enabled on your Azure subscription, the system collects security data from your multicloud and DevOps environments. Defender for Cloud uses the data to give insights, recommendations, and actions that help you protect your cloud workloads and resources. You can enable extra plans to get more advanced security features, such as Defender Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Defender for Databases, and Defender for Containers.
Reference: What is Microsoft Defender for Cloud?
Question: 241
Measured Skill: Describe the capabilities of Microsoft security solutions (35–40%)
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
(NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)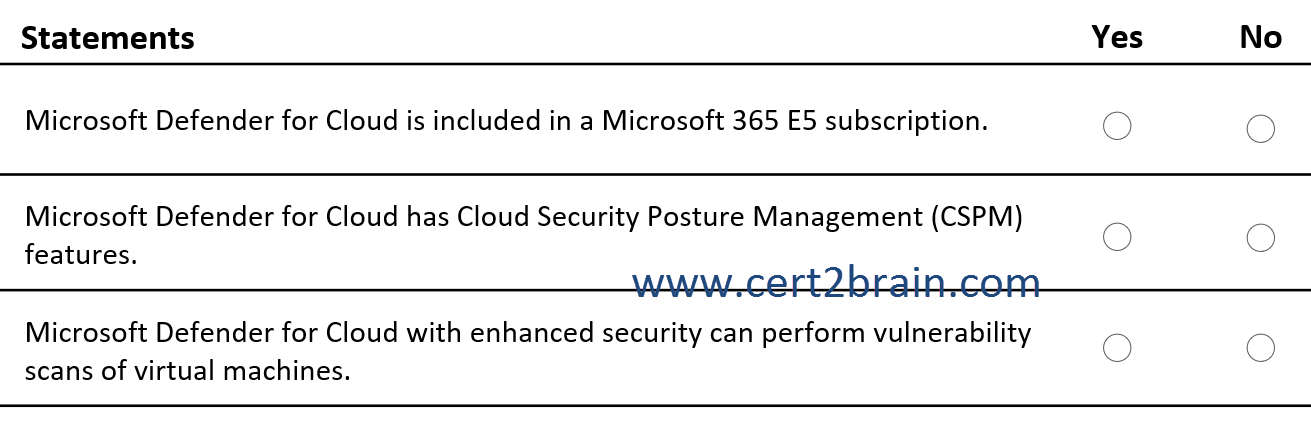
| A | Microsoft Defender for Cloud is included in a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription: Yes
Microsoft Defender for Cloud has Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) features: Yes
Microsoft Defender for Cloud with enhanced security can perform vulnerability scans of virtual machines: Yes |
| B | Microsoft Defender for Cloud is included in a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription: Yes
Microsoft Defender for Cloud has Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) features: Yes
Microsoft Defender for Cloud with enhanced security can perform vulnerability scans of virtual machines: No |
| C | Microsoft Defender for Cloud is included in a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription: Yes
Microsoft Defender for Cloud has Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) features: No
Microsoft Defender for Cloud with enhanced security can perform vulnerability scans of virtual machines: Yes |
| D | Microsoft Defender for Cloud is included in a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription: No
Microsoft Defender for Cloud has Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) features: Yes
Microsoft Defender for Cloud with enhanced security can perform vulnerability scans of virtual machines: No |
| E | Microsoft Defender for Cloud is included in a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription: No
Microsoft Defender for Cloud has Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) features: Yes
Microsoft Defender for Cloud with enhanced security can perform vulnerability scans of virtual machines: Yes |
| F | Microsoft Defender for Cloud is included in a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription: No
Microsoft Defender for Cloud has Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) features: No
Microsoft Defender for Cloud with enhanced security can perform vulnerability scans of virtual machines: No |
Correct answer: EExplanation:
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP), which is a unified solution that combines multiple cloud security tools to protect applications across their entire lifecycle. The solution provides a comprehensive view of your security posture across your cloud and on-premises resources. It also helps you secure multicloud and hybrid environments and integrates security into DevOps workflows. There are three core components:
Development Security Operations (DevSecOps) manages code-level security across multicloud and multi-pipeline environments.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) checks and improves the security posture of cloud resources.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) defends workloads such as virtual machines (VMs), containers, storage, databases, and serverless functions from threats.
Defender for Cloud uses its broader Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) capabilities to unify protections into one experience. Defender for Cloud embeds security early in the development lifecycle. It helps DevOps teams find misconfigurations, apply policies, and fix risks early.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps is a security tool and therefore doesn't require Microsoft 365 productivity suite licenses such as Microsoft 365 E5
When you enable Microsoft Defender for Cloud with enhanced security, specifically Defender for Servers Plan 1 or Plan 2, you unlock integrated vulnerability scanning capabilities for your virtual machines.
References:
What is Microsoft Defender for Cloud?
Microsoft Defender for Cloud pricing
Enable vulnerability scanning
Question: 242
Measured Skill: Describe the capabilities of Microsoft security solutions (35–40%)
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.
| A | Vulnerability articles from Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence (Defender TI) include a priority score. |
| B | Vulnerability articles from Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence (Defender TI) include Intel profiles. |
| C | Vulnerability articles from Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence (Defender TI) include Intel projects. |
| D | Vulnerability articles from Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence (Defender TI) include Microsoft Secure Score. |
Correct answer: AExplanation:
Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence (Defender TI) is a platform that streamlines triage, incident response, threat hunting, vulnerability management, and threat intelligence analyst workflows when conducting threat infrastructure analysis and gathering threat intelligence.
Articles are narratives that provide insight into threat actors, tooling, attacks, and vulnerabilities. Defender TI articles aren't blog posts about threat intelligence; while these articles summarize different threats, they also link to actionable content and key IOCs to help users take action. Having this technical information in the threat summaries lets users continually track threat actors, tooling, attacks, and vulnerabilities as they change.
Each vulnerability article contains:
- A description of the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
- A list of affected components
- Tailored mitigation procedures and strategies
- Related intelligence articles
- References in deep and dark web chatter
- Other key observations
These articles provide deeper context and actionable insights behind each CVE, letting users understand and mitigate these vulnerabilities more quickly.
Vulnerability articles also include a Defender TI priority score and severity indicator. The Defender TI priority score is a unique algorithm that reflects the priority of a CVE based on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) score, exploits, chatter, and linkage to malware. It evaluates the recency of these components so you can understand which CVEs should be remediated first.
Reference: What is Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence (Defender TI)?
Question: 243
Measured Skill: Describe the capabilities of Microsoft compliance solutions (20–25%)
Which Microsoft Purview feature allows users to identify content that should be protected?| A | Sensitivity Labels |
| B | Data loss prevention |
| C | eDiscovery |
| D | Insider Risks |
Correct answer: AExplanation:
Sensitivity labels in Microsoft Purview Information Protection allow users to classify and tag content based on its sensitivity level—such as Confidential, Restricted, or Public. These labels help identify content that needs protection, and can automatically apply encryption, access restrictions, and content markings like watermarks or headers. Labels can be applied manually by users or automatically based on rules and conditions, making them a proactive tool for data governance and compliance.
Reference: Learn about sensitivity labels
Question: 244
Measured Skill: Describe the concepts of security, compliance, and identity (10–15%)
In the shared responsibility model, for what is Microsoft responsible when managing Azure virtual machines?| A | Updating the firmware of the disk controller. |
| B | Updating installed applications. |
| C | Configuring the permissions for shared folders. |
| D | Updating the operating system. |
Correct answer: AExplanation:
As you consider and evaluate public cloud services, it's critical to understand the shared responsibility model and which security tasks the cloud provider handles and which tasks you handle. The workload responsibilities vary depending on whether the workload is hosted on Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), or in an on-premises datacenter.
In an on-premises datacenter, you own the whole stack. As you move to the cloud some responsibilities transfer to Microsoft. The following diagram illustrates the areas of responsibility between you and Microsoft, according to the type of deployment of your stack.
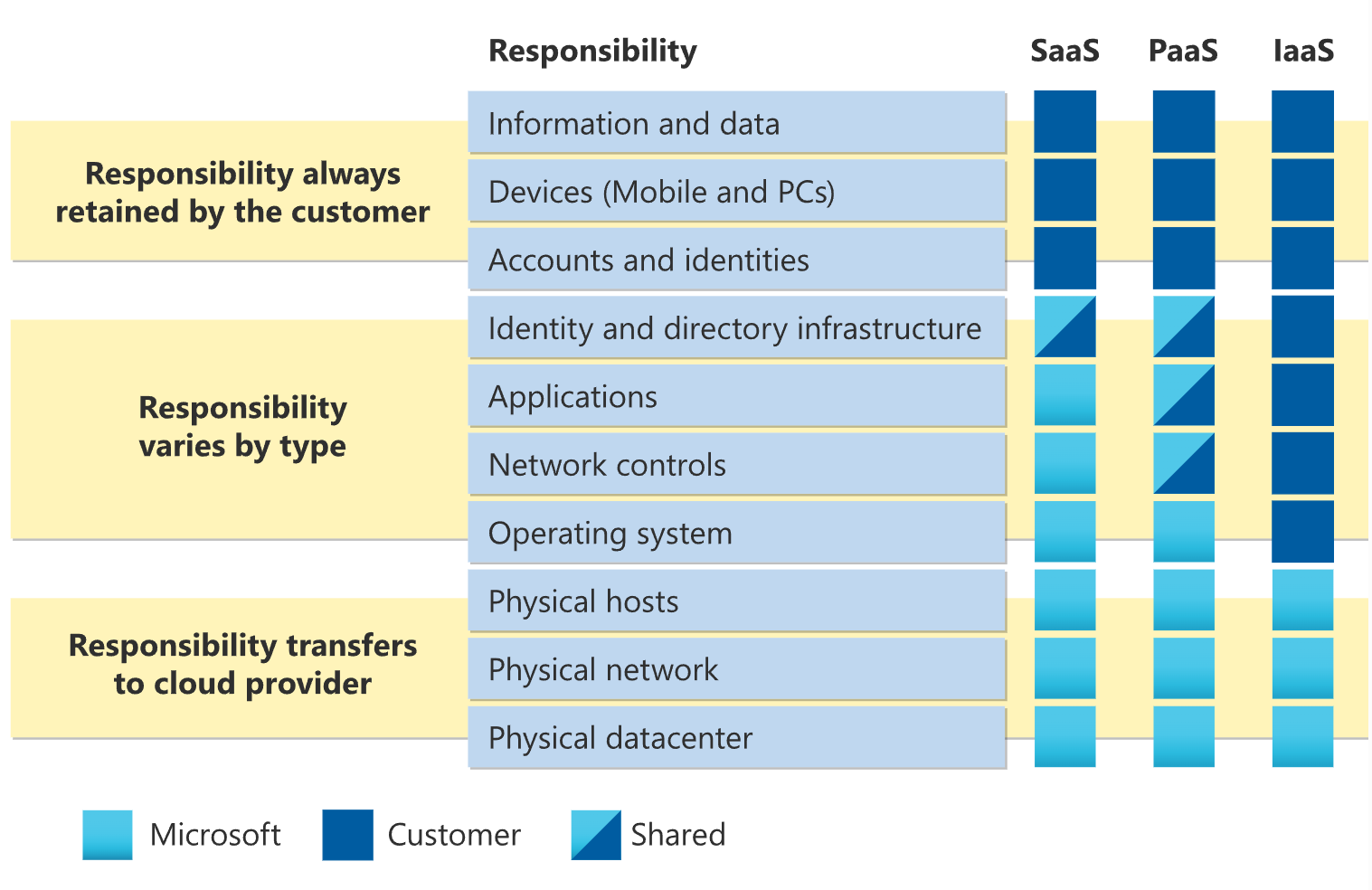
For all cloud deployment types, you own your data and identities. You're responsible for protecting the security of your data and identities, on-premises resources, and the cloud components you control. Cloud components you control vary by service type.
Regardless of the type of deployment, you always retain the following responsibilities:
- Data
- Endpoints
- Account
- Access management
Reference: Shared responsibility in the cloud